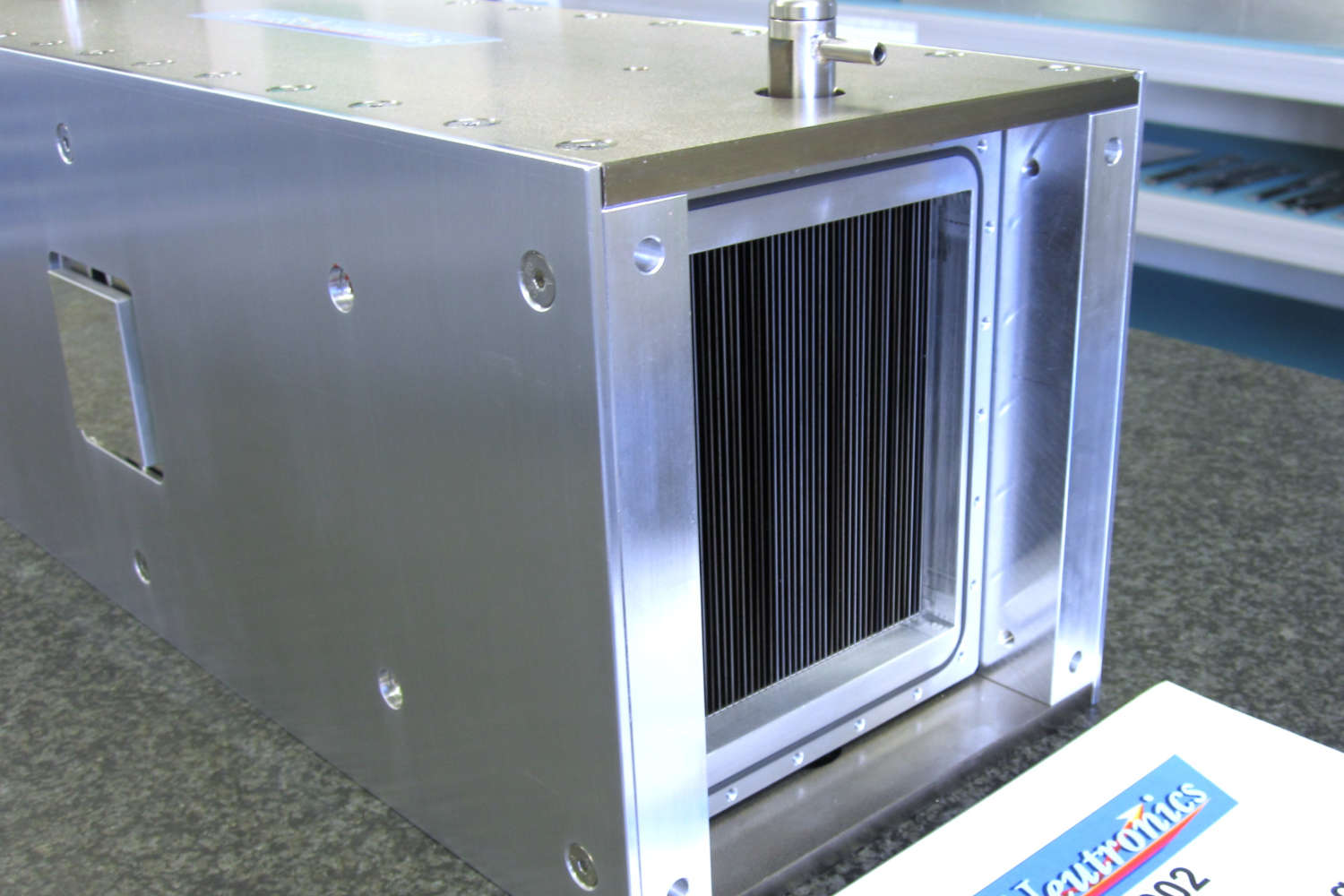
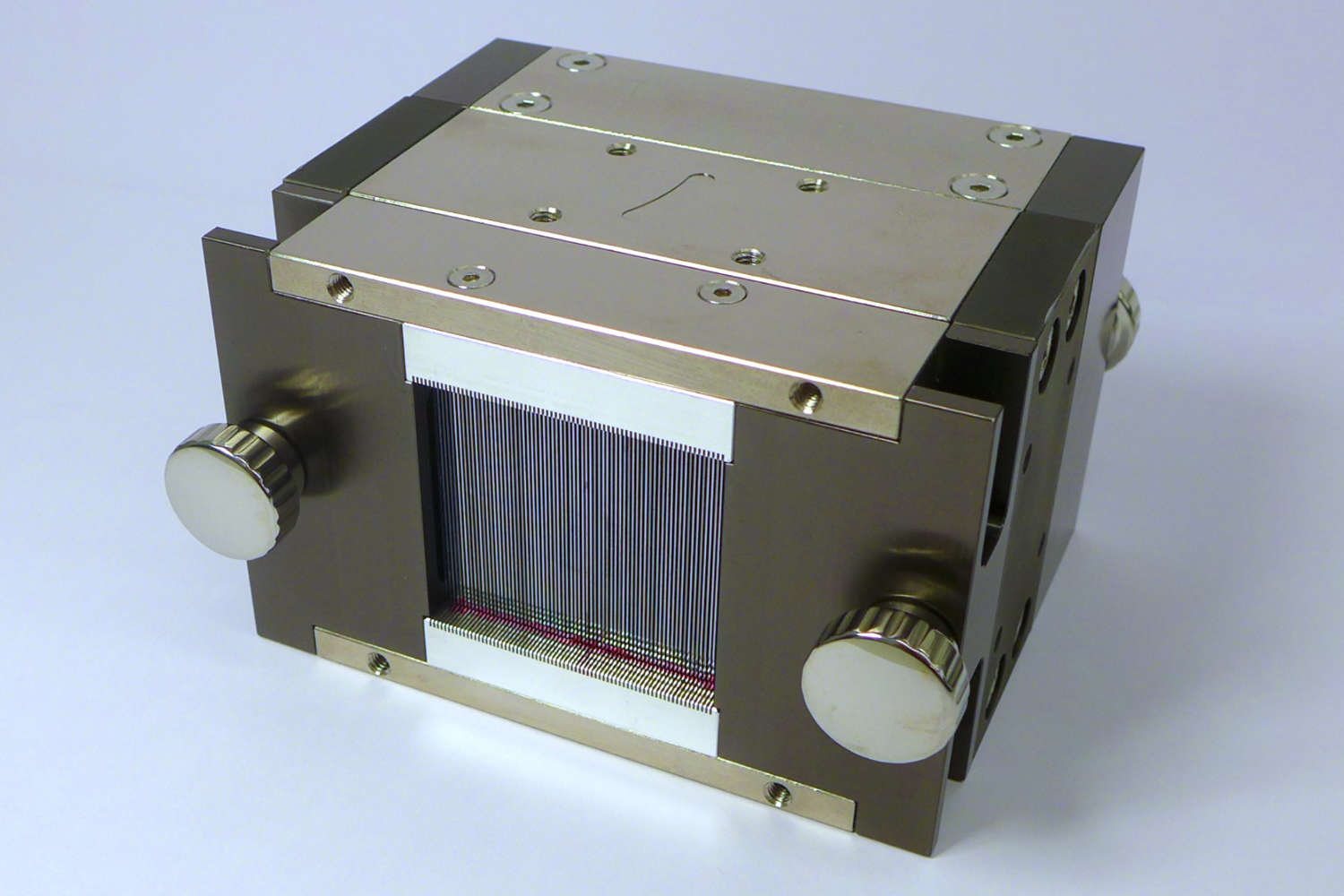
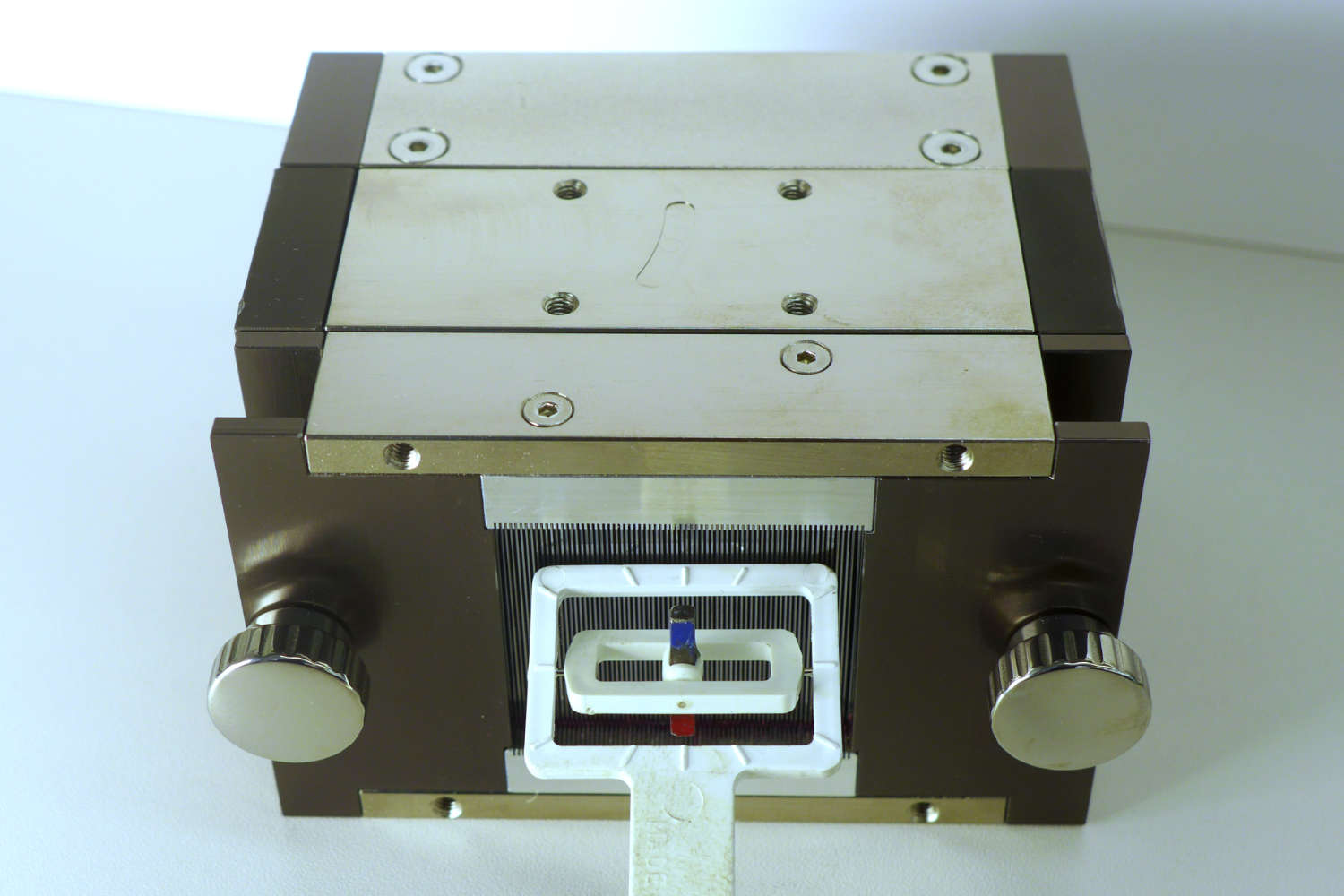
Polarizing benders polarize neutron beams across a wide wavelength range. Macro benders use curved, supermirror-coated guides; micro benders are compact, using bent thin boron glass lamellas. Solid-state benders with Si wafers offer high efficiency in transmission geometry, while reflection geometry increases divergence and requires beamline adjustments. All designs support flexible applications.
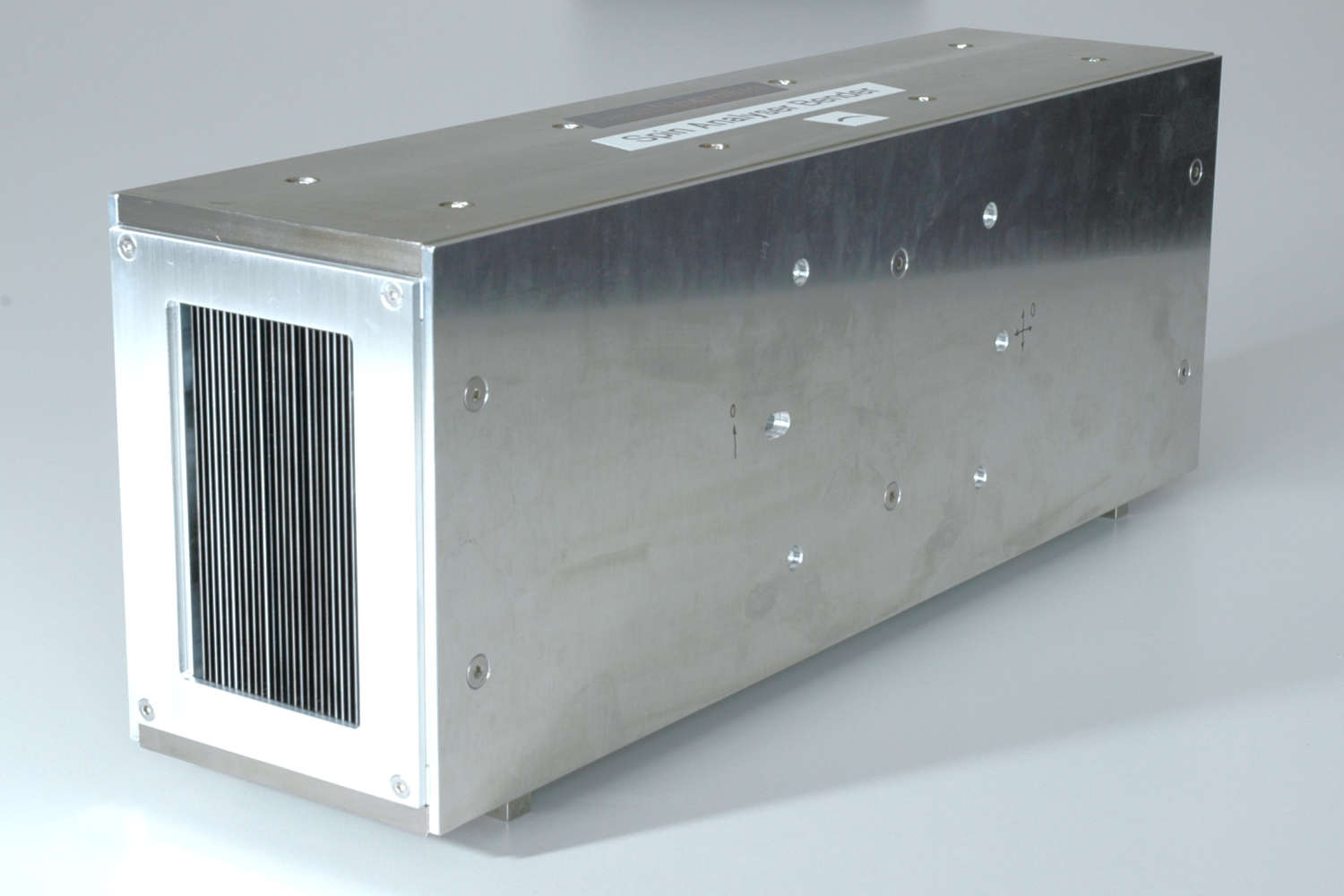
Polarizing benders are neutron optical devices designed to polarize neutron beams across a broad wavelength range. They are categorized into macro benders and micro benders, each optimized for different applications and spatial constraints.
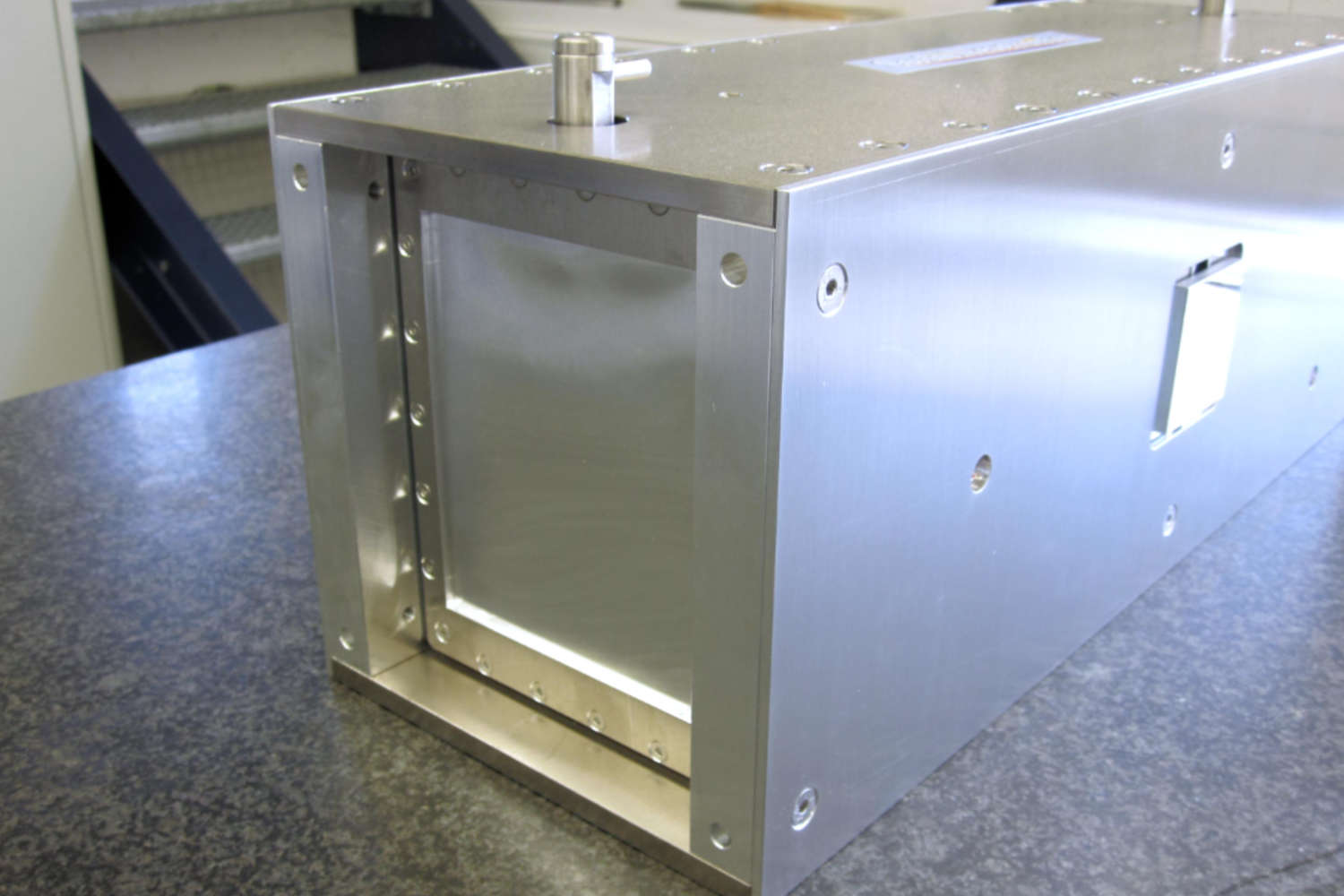
- Macro benders resemble curved neutron guides eventually segmented into few multiple parallel channels, each coated with Fe/Si polarizing supermirrors. These structures enable efficient spin selection over extended beam paths.
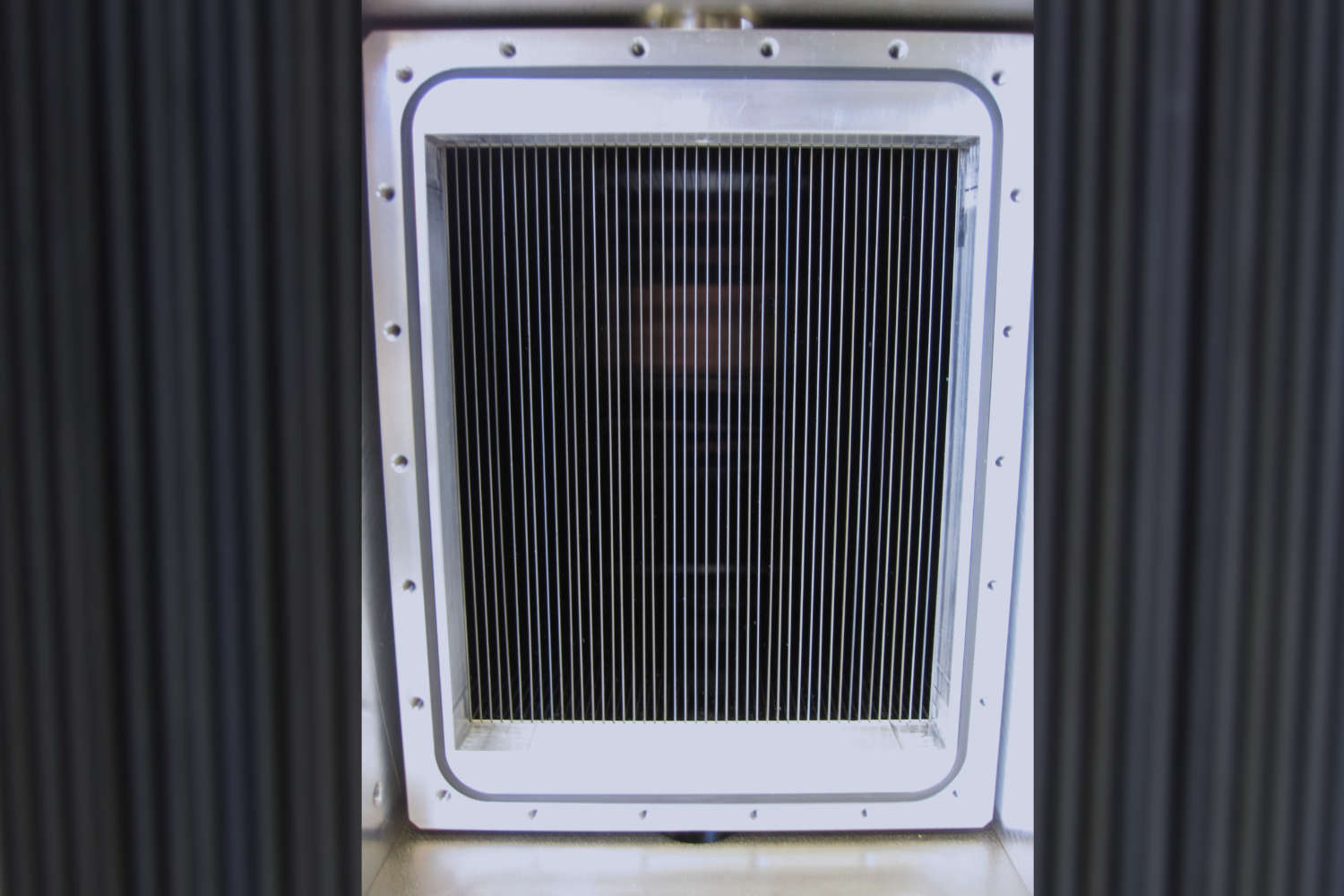
- Micro benders are compact devices composed of thin boron-containing glass lamellas (typically 0.3 mm thick), also coated with polarizing supermirrors. The narrow channel width—just a few millimeters—allows for space-saving integration. However, the transmitted beam is deflected from the optical axis.
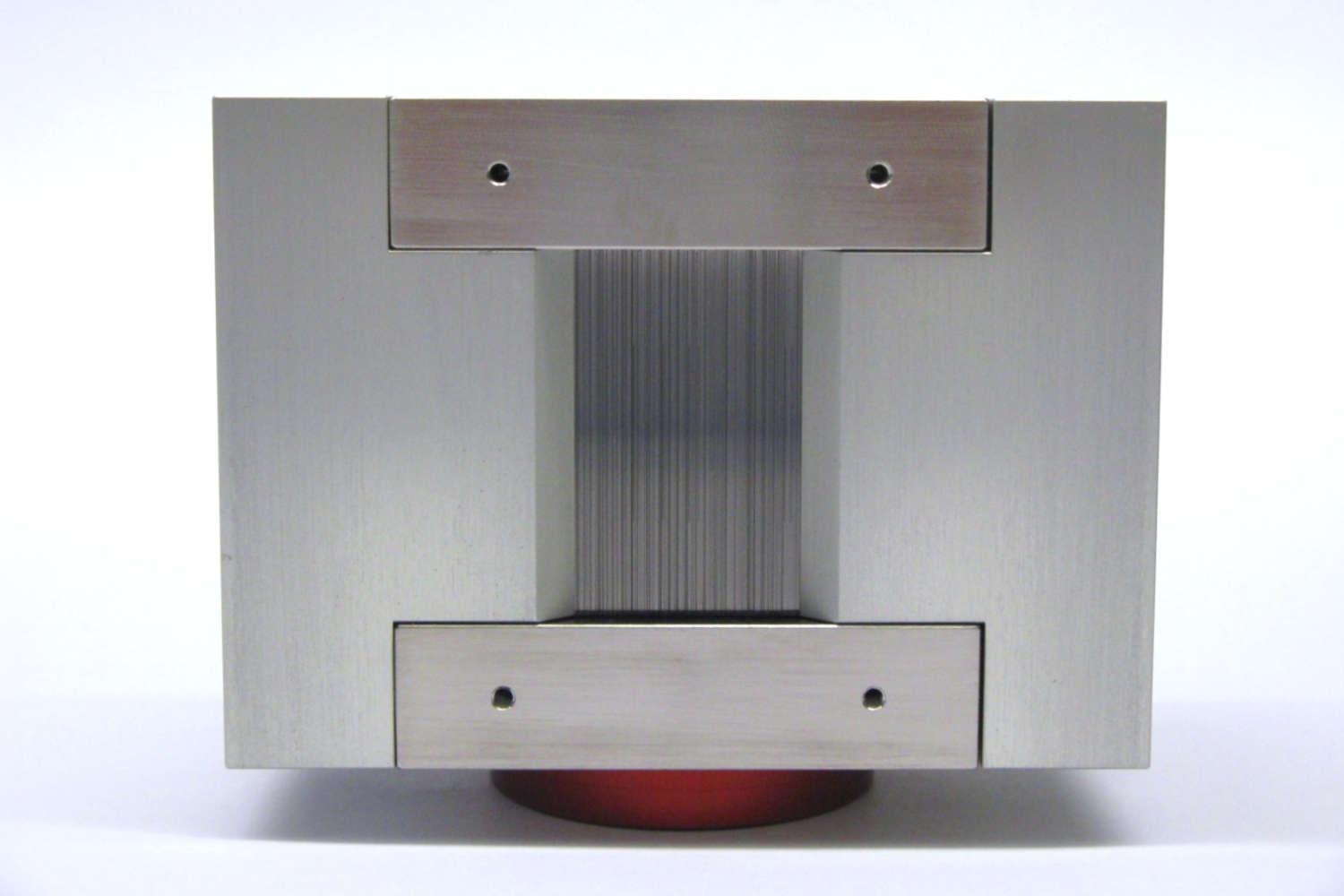
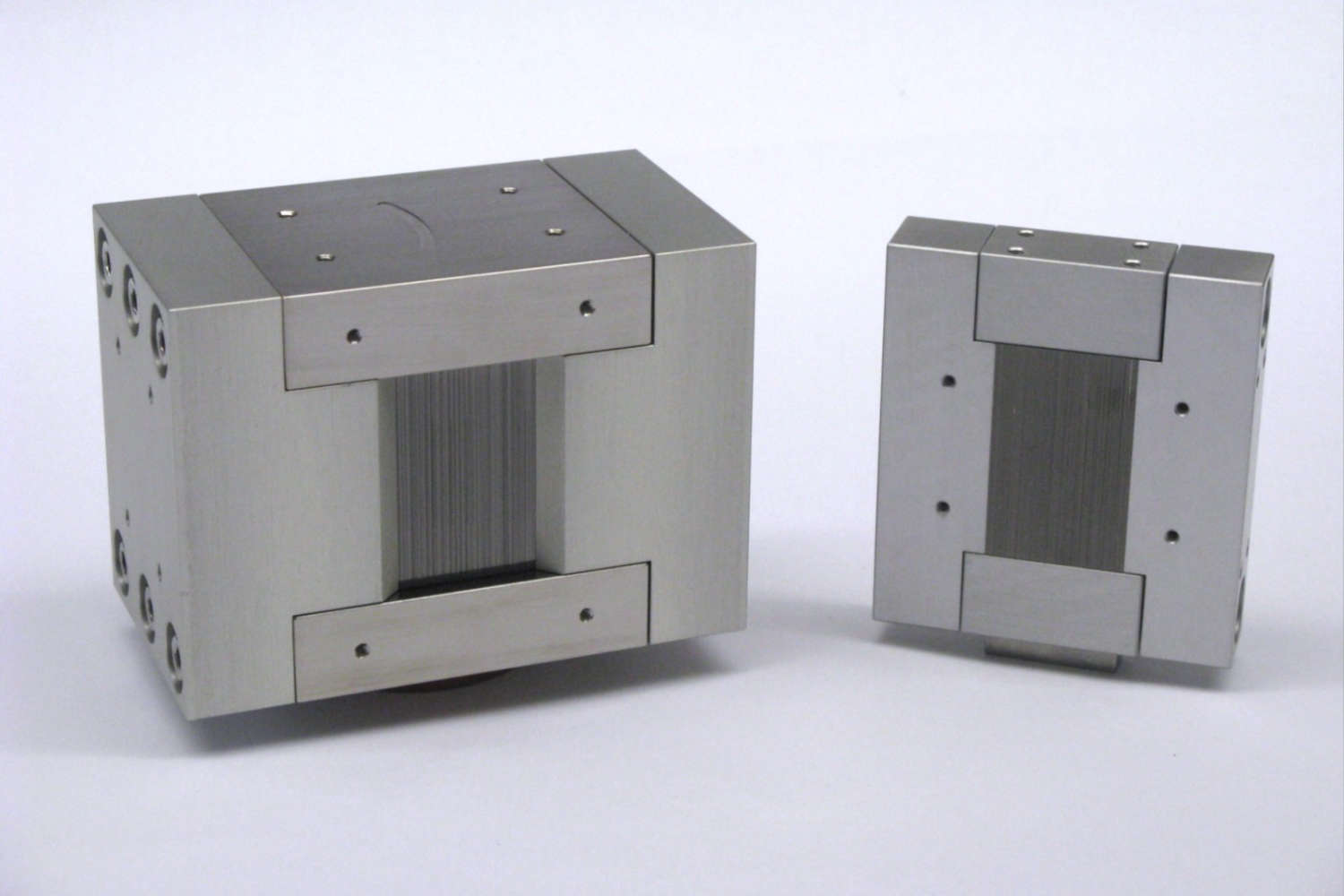
- Solid-state benders offer an alternative approach, using stacks of silicon wafers (0.15–0.6 mm thick) coated with polarizing supermirrors. In transmission geometry (without absorption layers), they preserve the neutron phase space and offer high efficiency. When absorption layers are added, the benders operate in reflection geometry, increasing beam divergence and deflecting the beam from its optical axis. This often necessitates time-consuming beamline adjustments. Despite these considerations, solid-state benders are highly convenient and user-friendly, making them suitable for a wide range of neutron polarization applications.
Technical highlights
- Coating Materials
Iron (Fe), Silicon (Si) - m-Value Range
1 ≤ m ≤ 6.0 - Polarization Efficiency
~97% - Transmission of Polarized Beam
~50-80% - Typical deflection angles
θ ≈ 1.2° - Optical Geometry
Transmission or reflection - Beam size (from to)
– Small benders: 30 mm (width) × 30 mm (height)
– Large benders: 100 mm (width) × 200 mm (height) - Length of benders
30 mm ≤ L ≤ 7000 mm - Thickness of blades
0.15 ≤ t ≤ 0.78 mm - Magnetizing Field
Approx. 50 mT (integrated in casing)