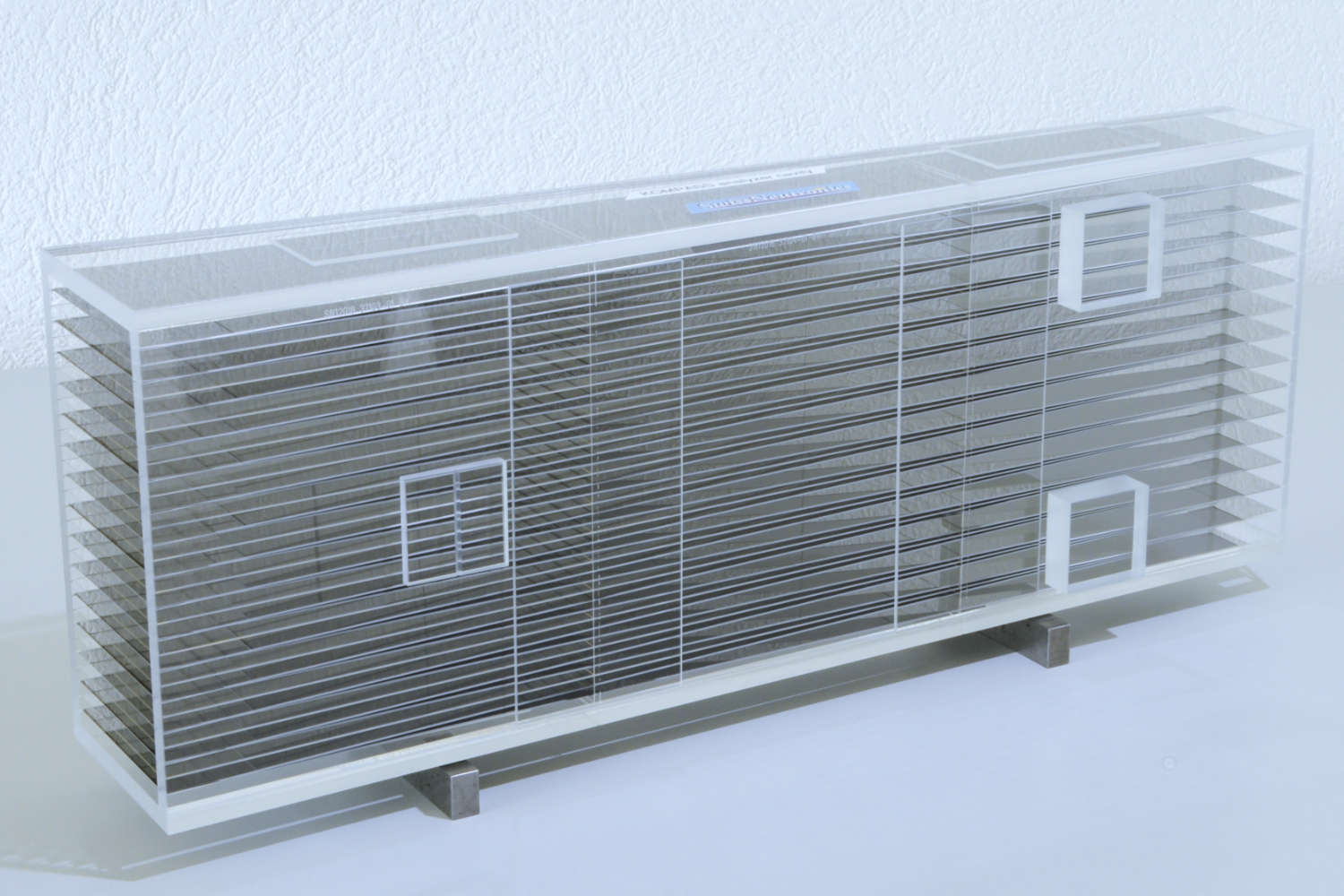
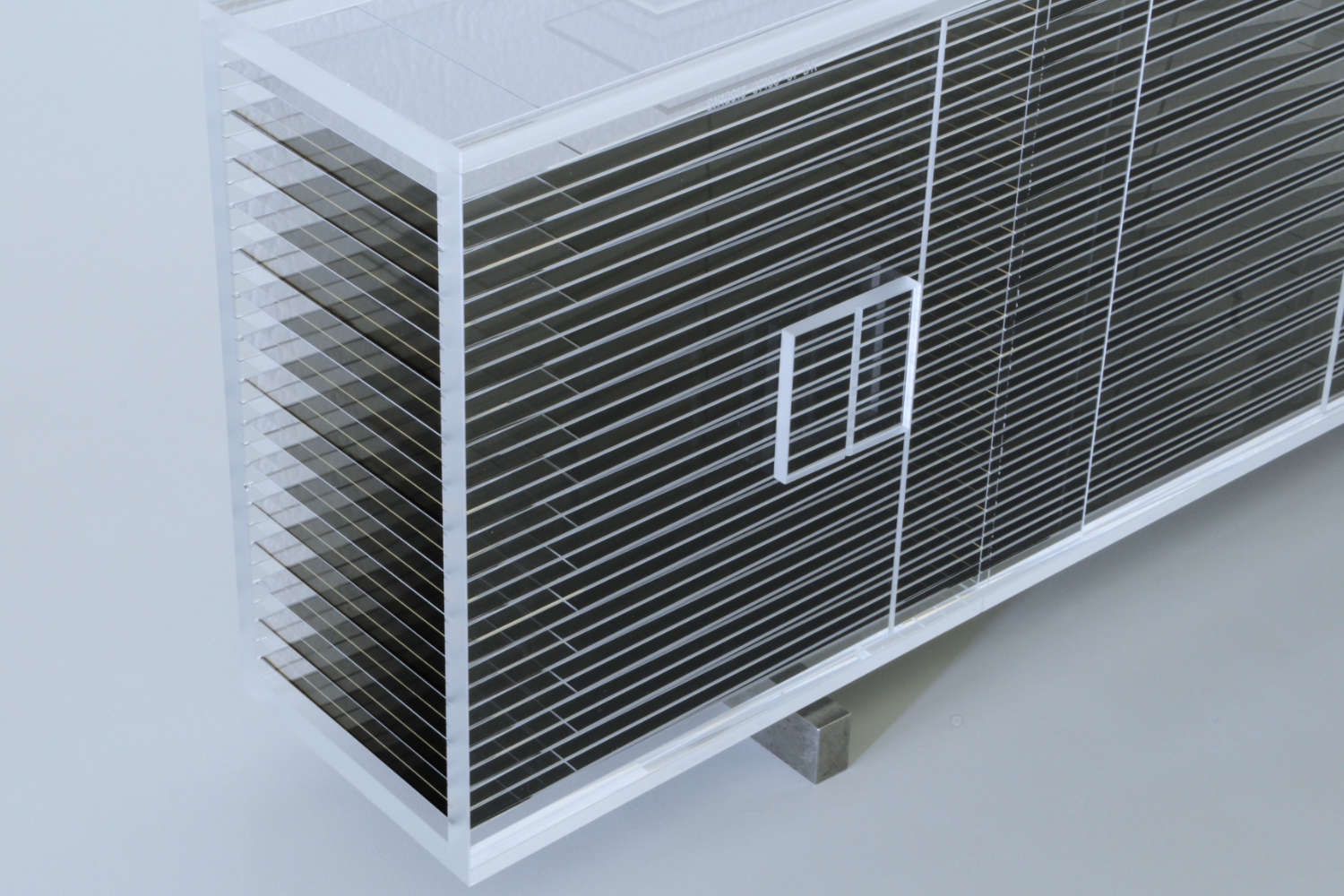
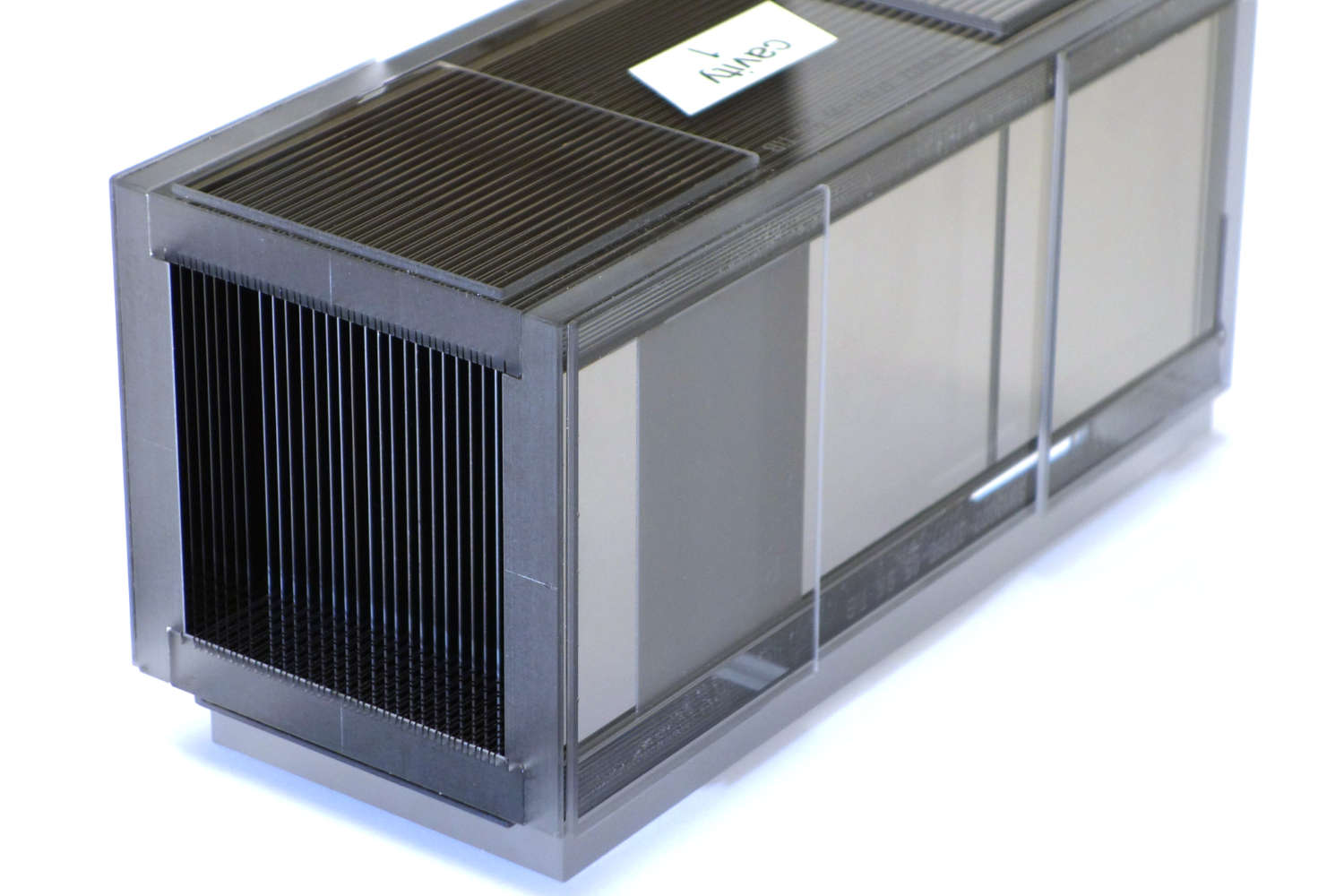
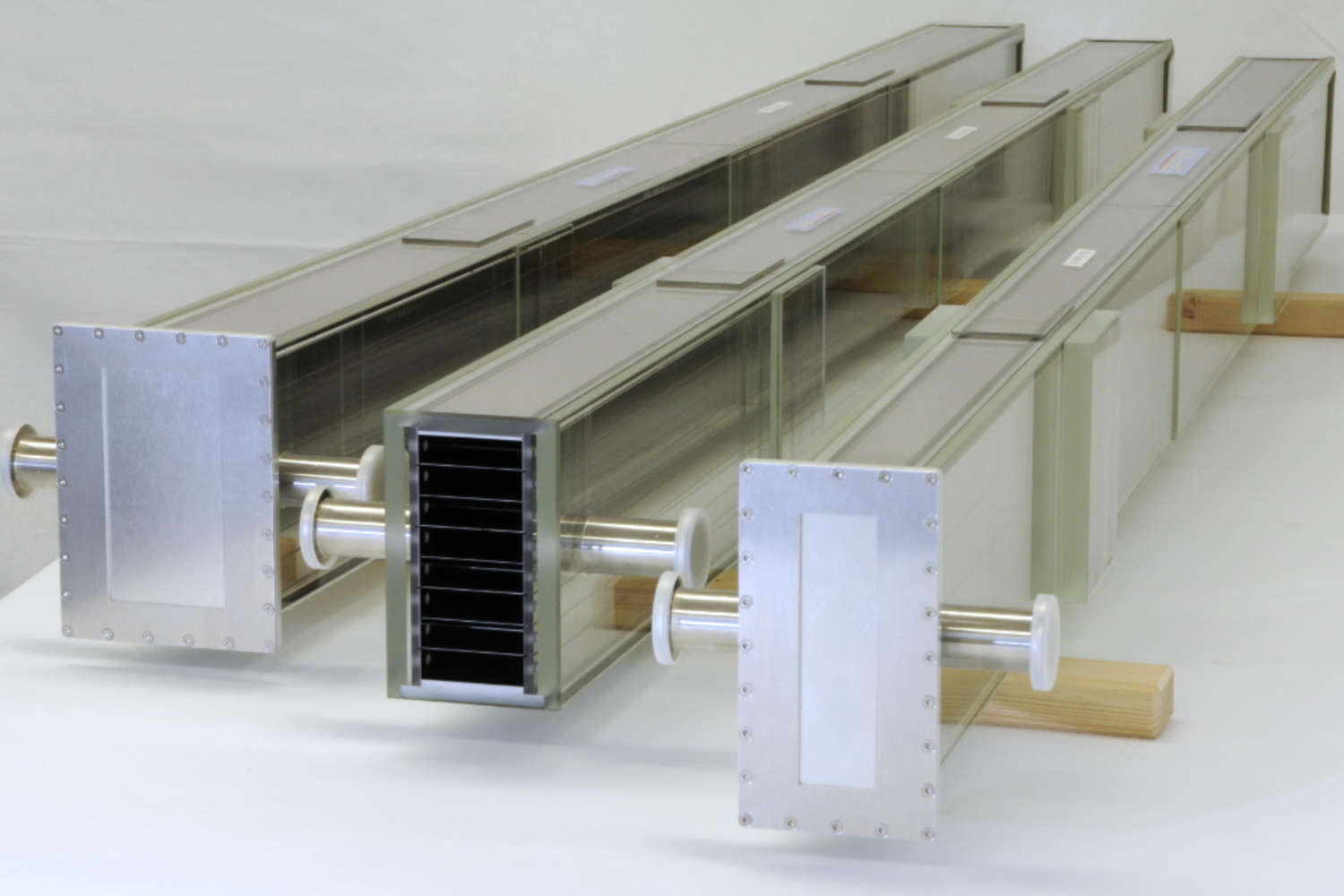
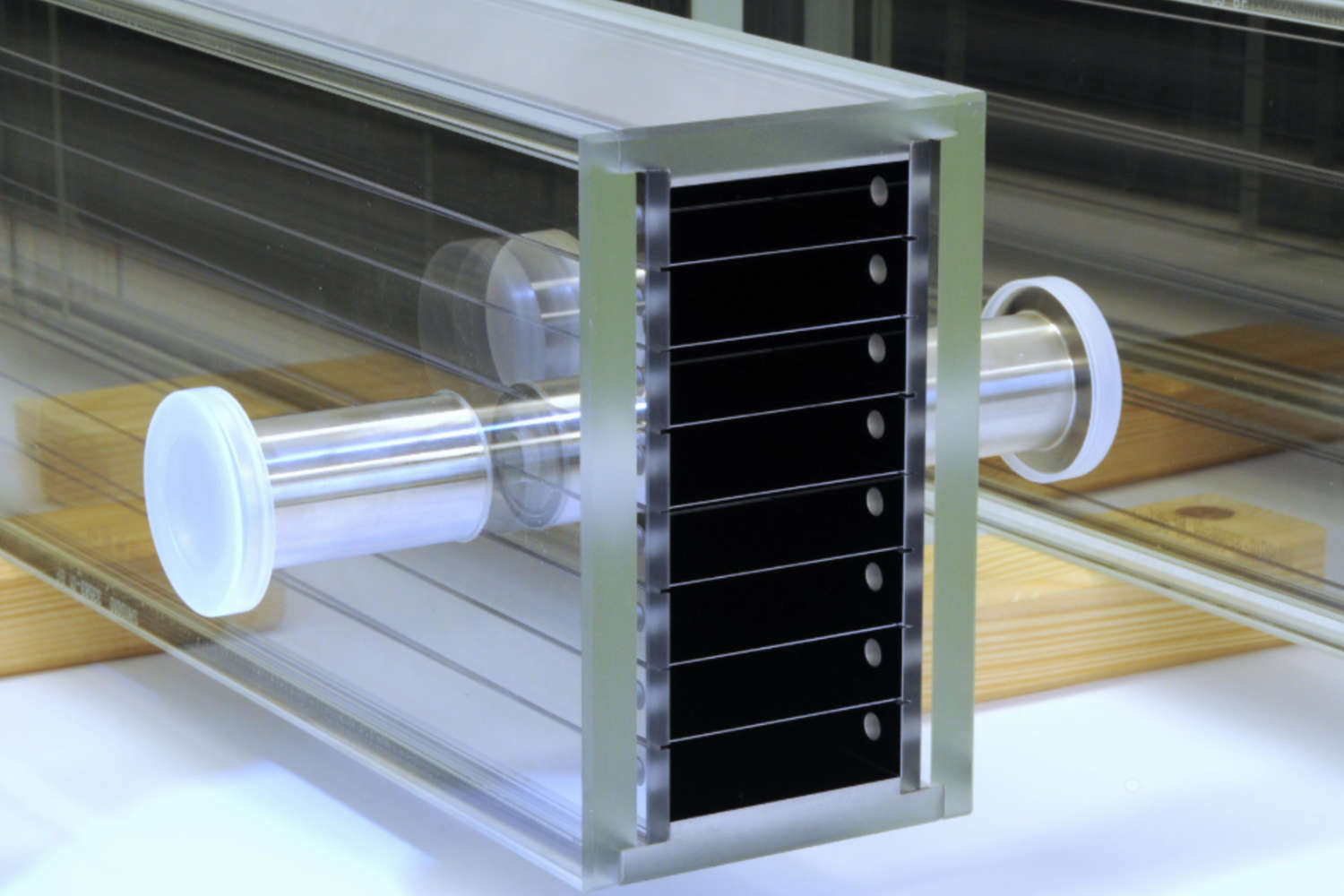
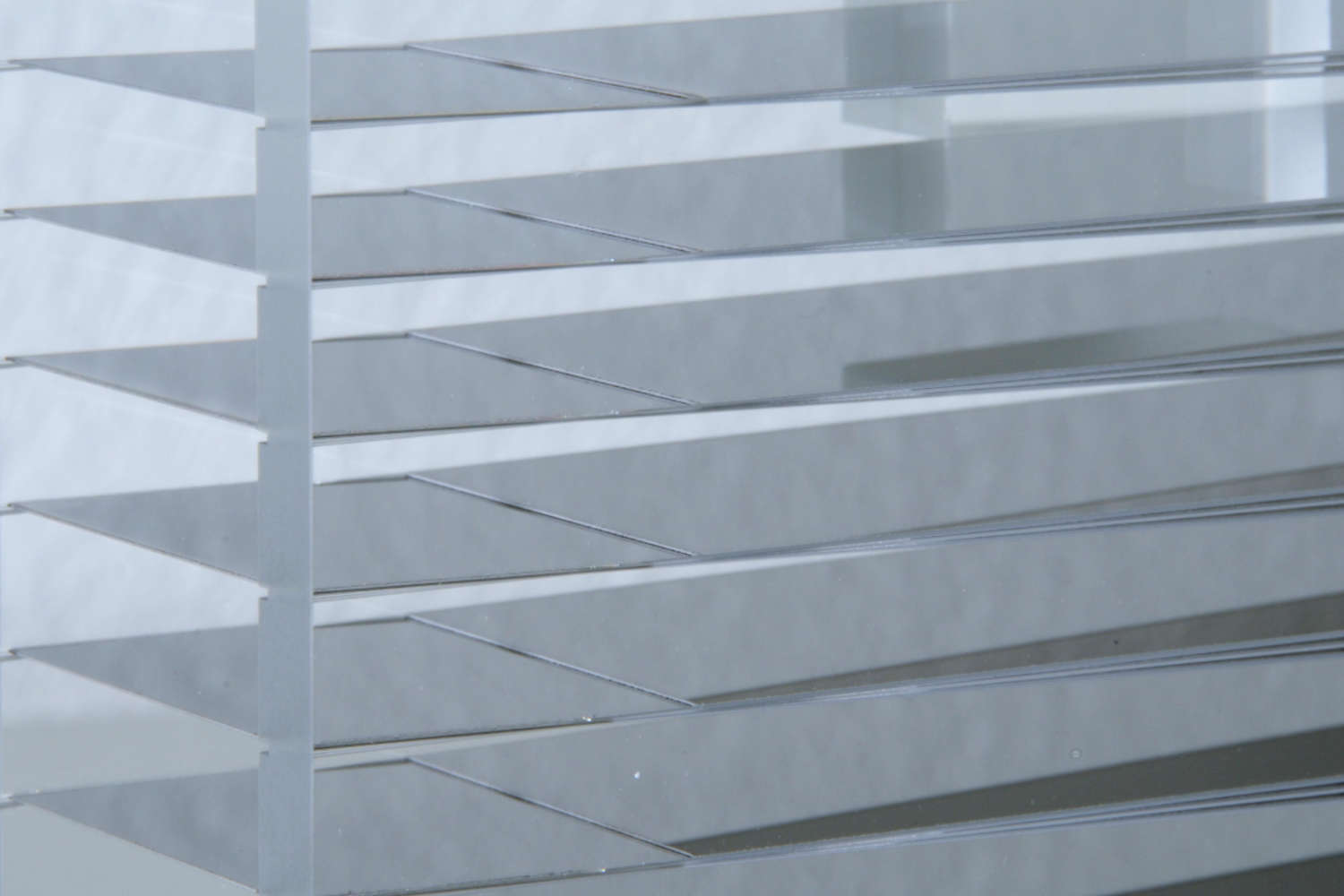
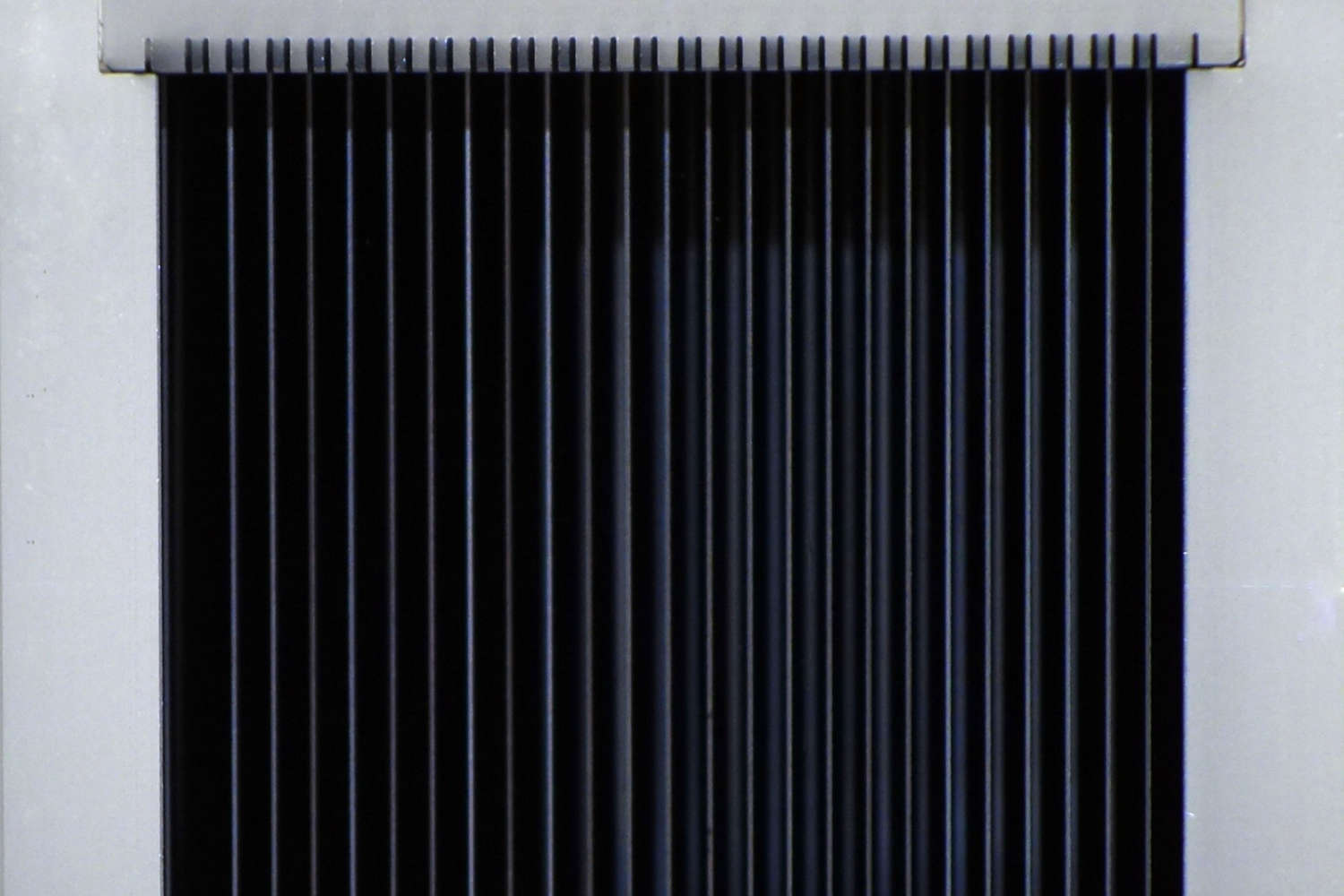
Polarizing cavities use spin-dependent neutron transmission through supermirrors on silicon wafers. One spin state is transmitted, the other reflected. V-shaped wafer arrangements shorten the device length. Multiple parallel channels cover wider beams, while serial V-configurations enhance polarization efficiency—ideal for experiments needing high polarization purity, like neutron scattering or fundamental physics.
The principle of polarizing cavities relies on the spin-dependent transmission of neutrons through a polarizing supermirror, which is typically deposited on a silicon substrate known as a polarizing wafer. These supermirrors are engineered to selectively transmit neutrons of one spin orientation while reflecting those of the opposite spin out of the beam path. This selective filtering enables the generation of a polarized neutron beam. To optimize the compactness of the device while maintaining its functional width, the polarizing wafers are arranged in a V-shaped geometry. This configuration enables the polarization of a neutron beam over a shorter physical length.
To accommodate wider neutron beams, multiple parallel channels are constructed, each incorporating its own V-shaped polarizing unit. This modular approach enables scalable coverage of the beam cross-section. Furthermore, placing two or more V-shaped units in series—effectively creating a multi-stage polarizing cavity—significantly improves the polarization efficiency. Each successive stage further filters the beam, reducing the fraction of incorrectly polarized neutrons. This serial arrangement is particularly useful in applications requiring high polarization purity, such as neutron scattering experiments or fundamental physics research involving spin-dependent interactions.
Technical highlights
- Coating Materials
Iron (Fe), Silicon (Si) - m-Value Range
1 ≤ m ≤ 6.0 - Polarization Efficiency
– Single V: ~92%
– Double V: ~98% - Transmission of Polarized Beam
– Single V: ~80%
– Double V: ~70% - Typical Beam Size (from to)
– Small cavities: 30 mm (width) × 30 mm (height)
– Large cavities: 100 mm (width) × 200 mm (height) - Polarizer Length
200 mm ≤ L ≤ 7000 mm - Magnetizing Field
Approx. 50 mT (integrated in casing) - Spin Selection
Compatible with RF spin-flipper systems