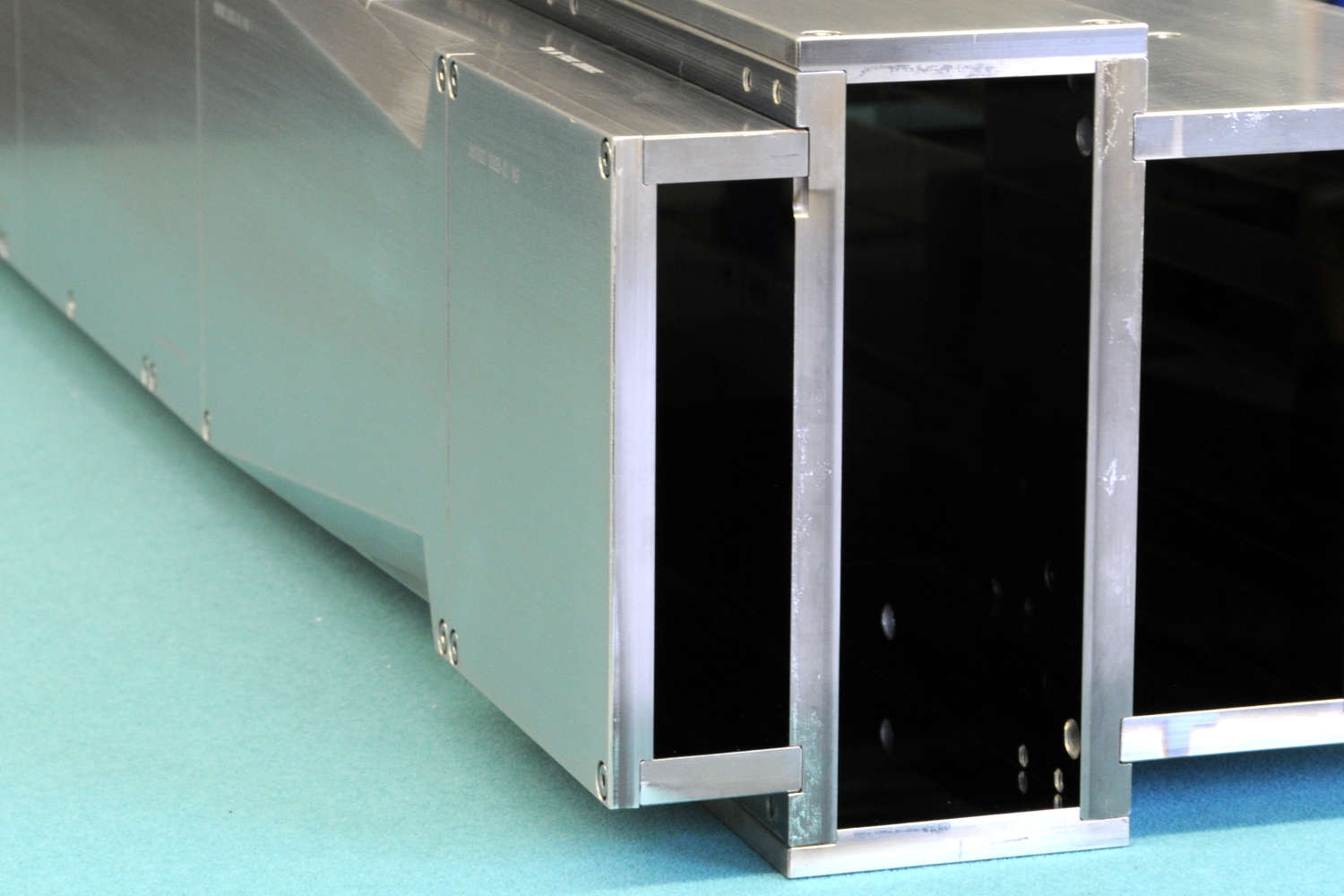
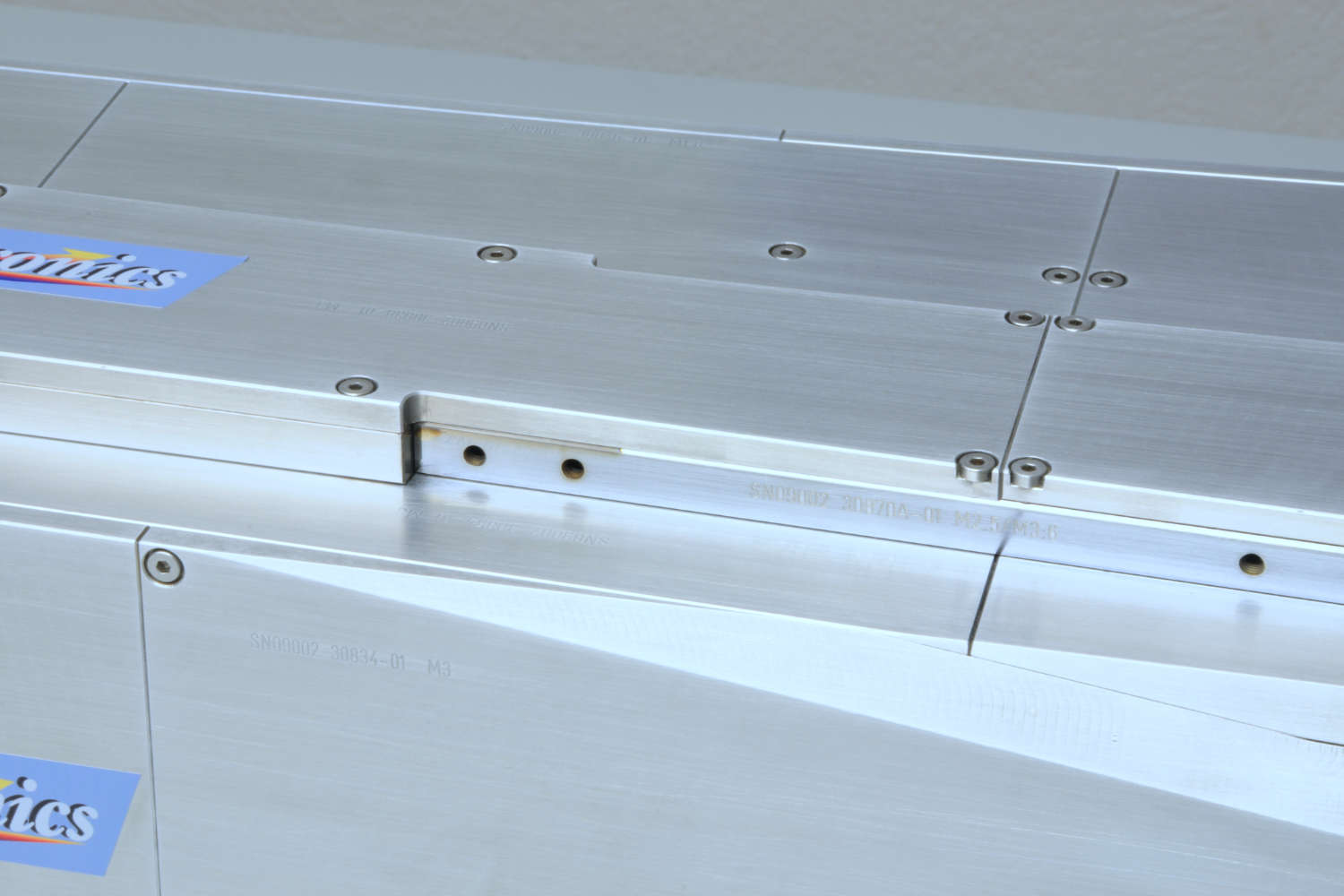
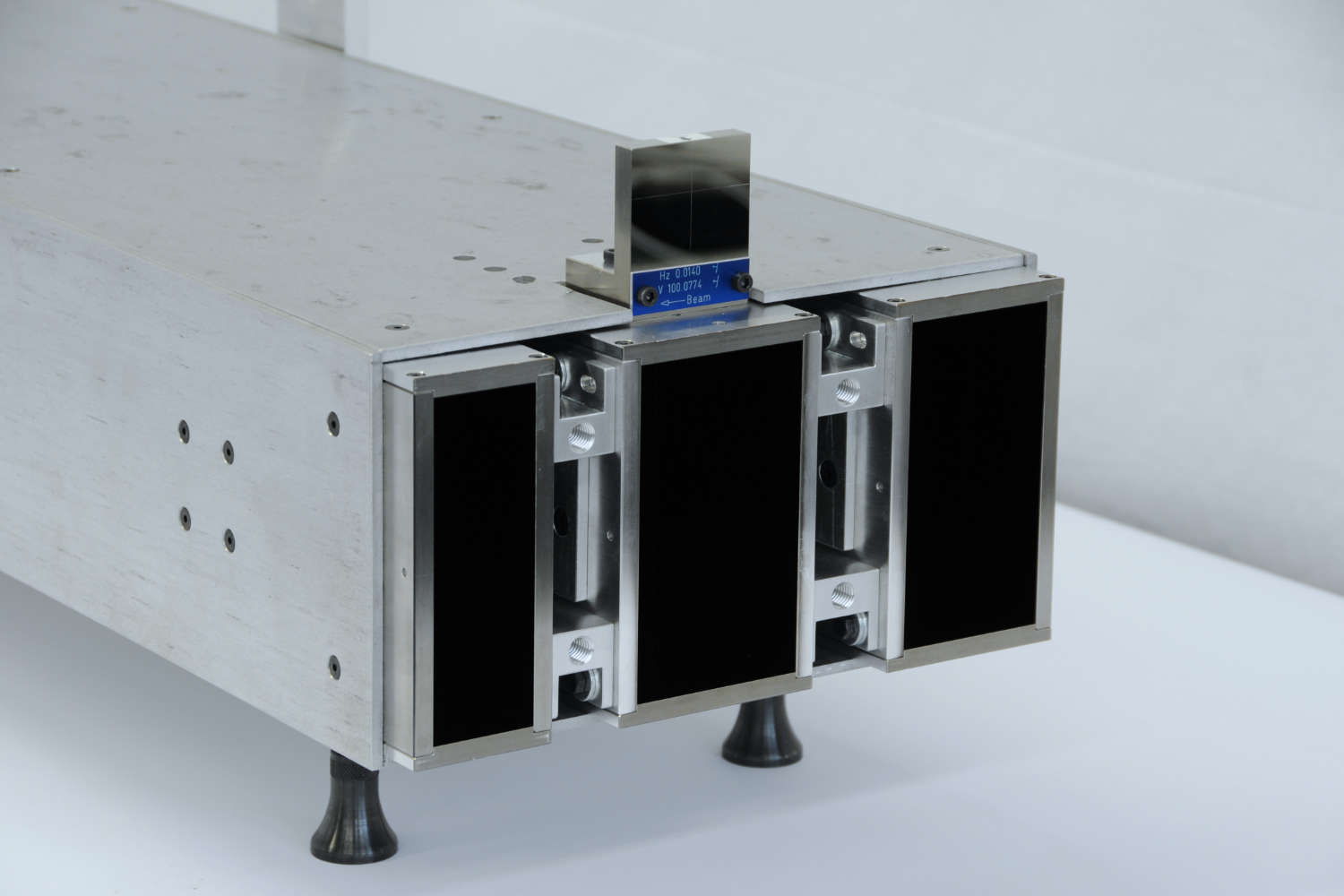
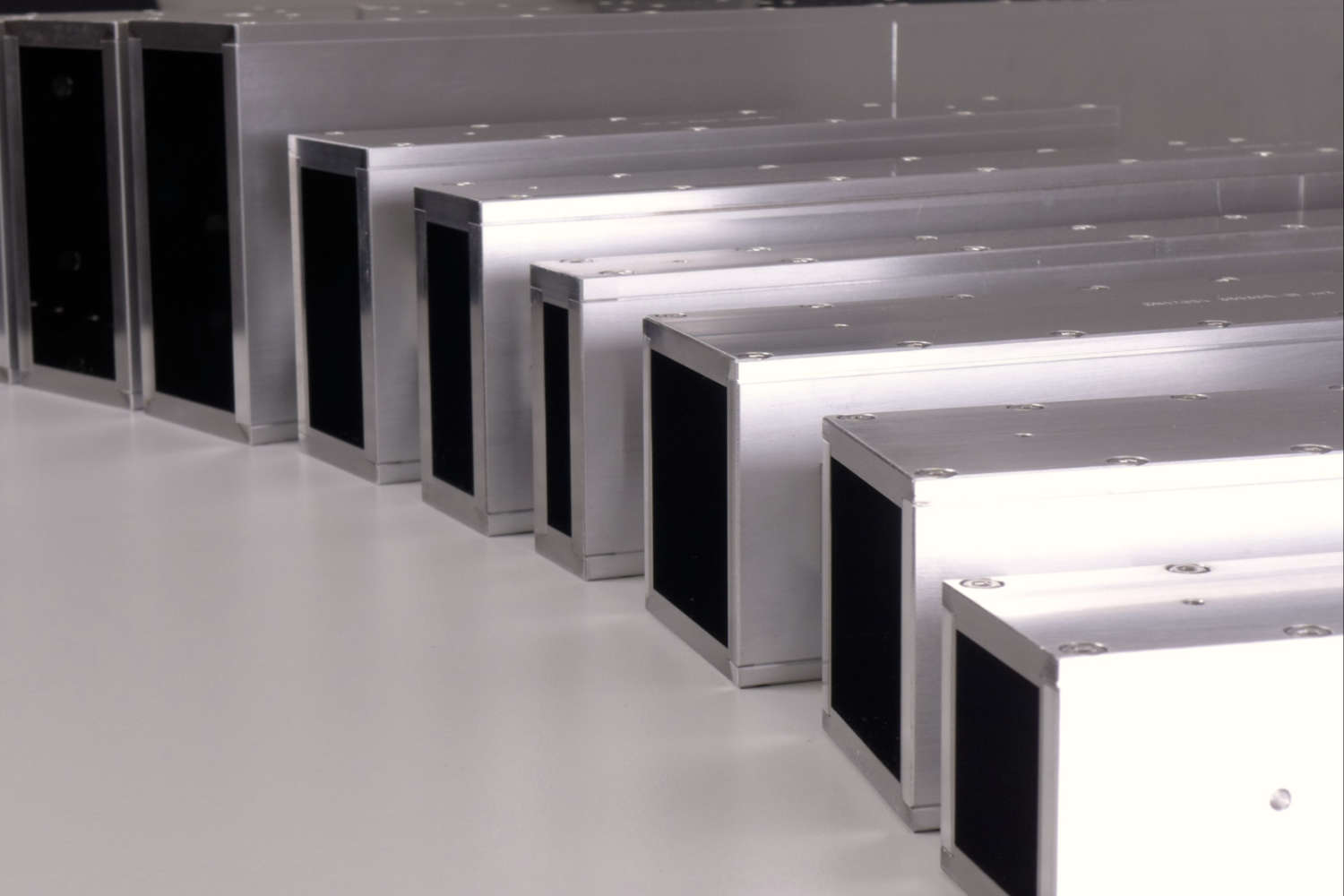
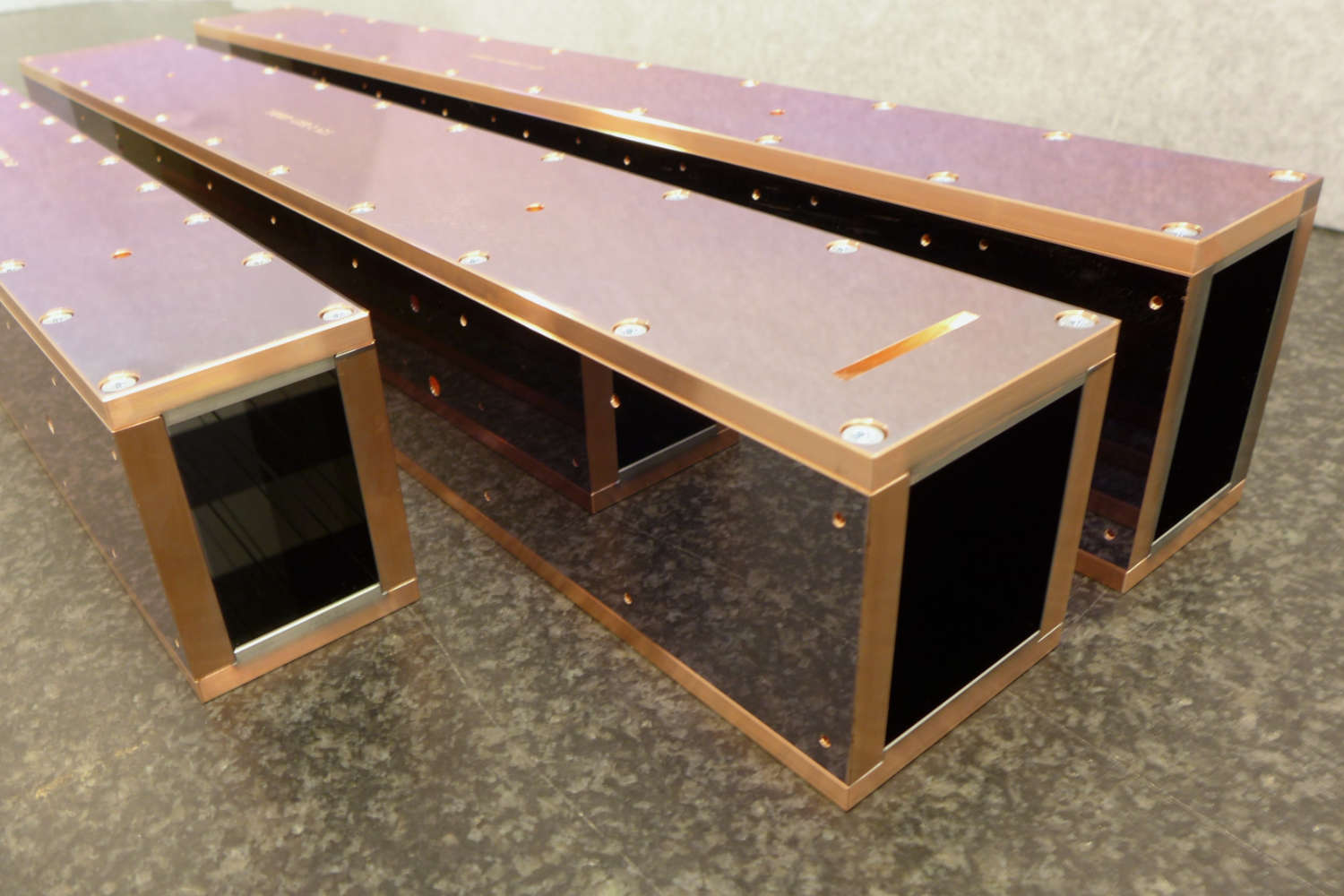
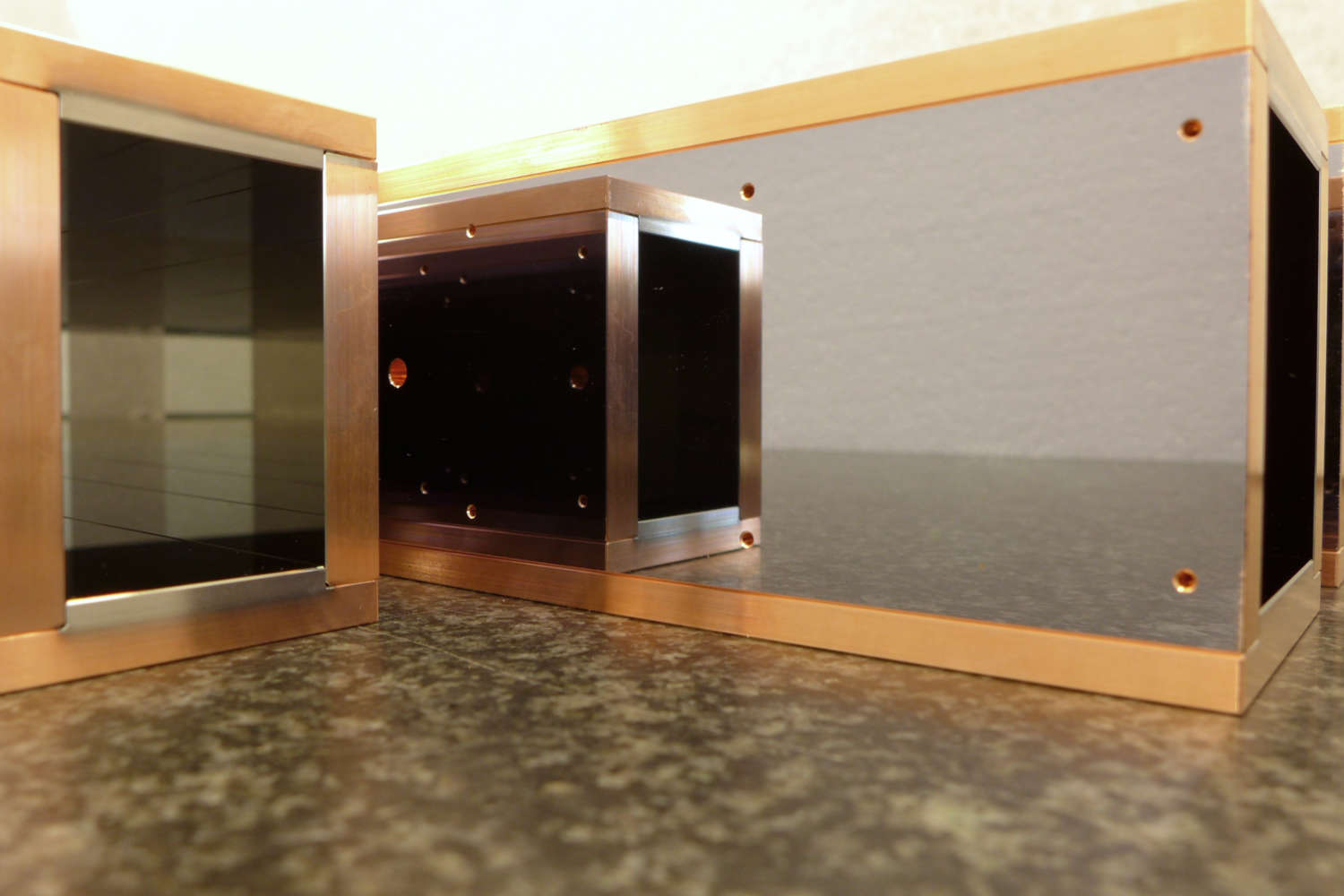
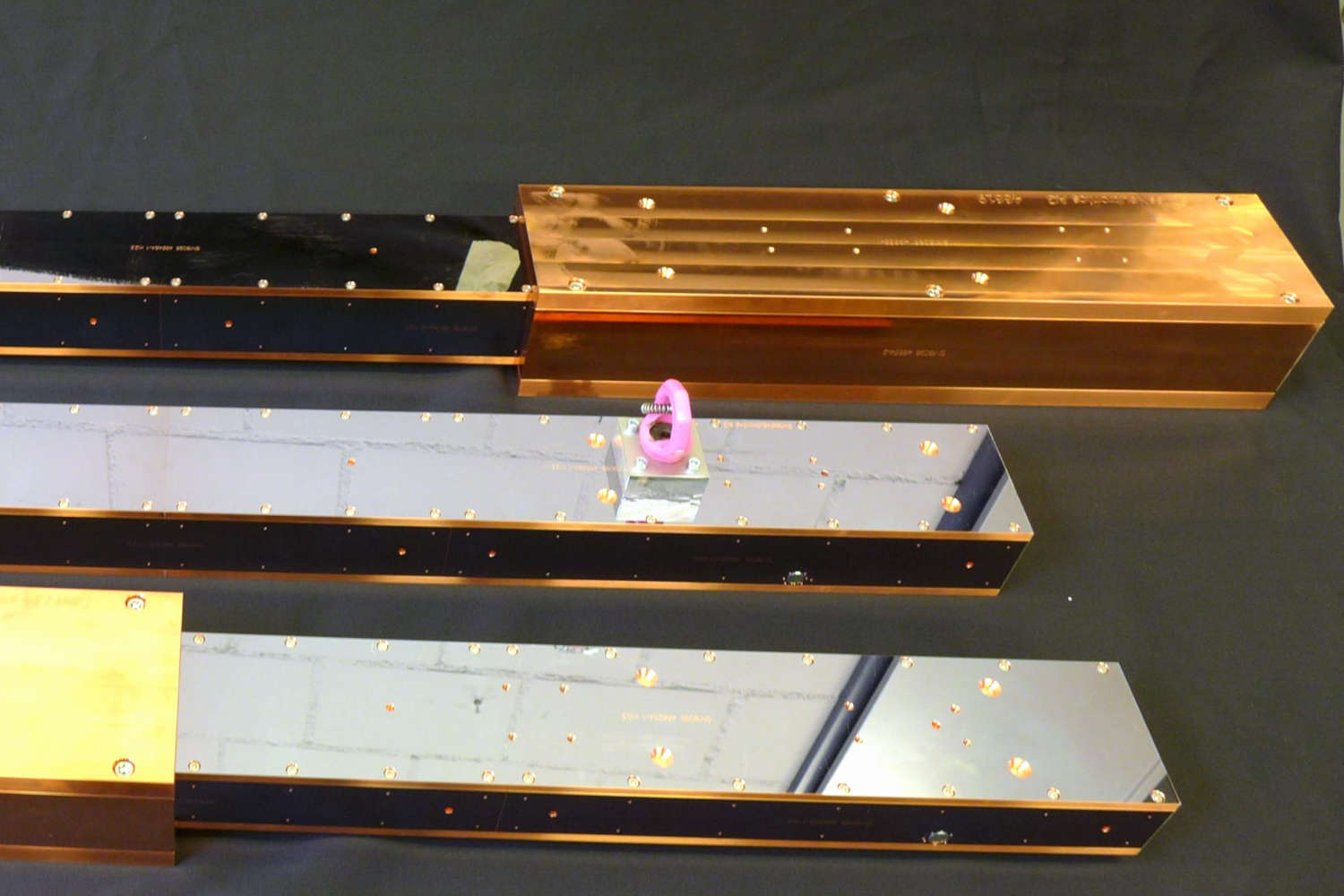
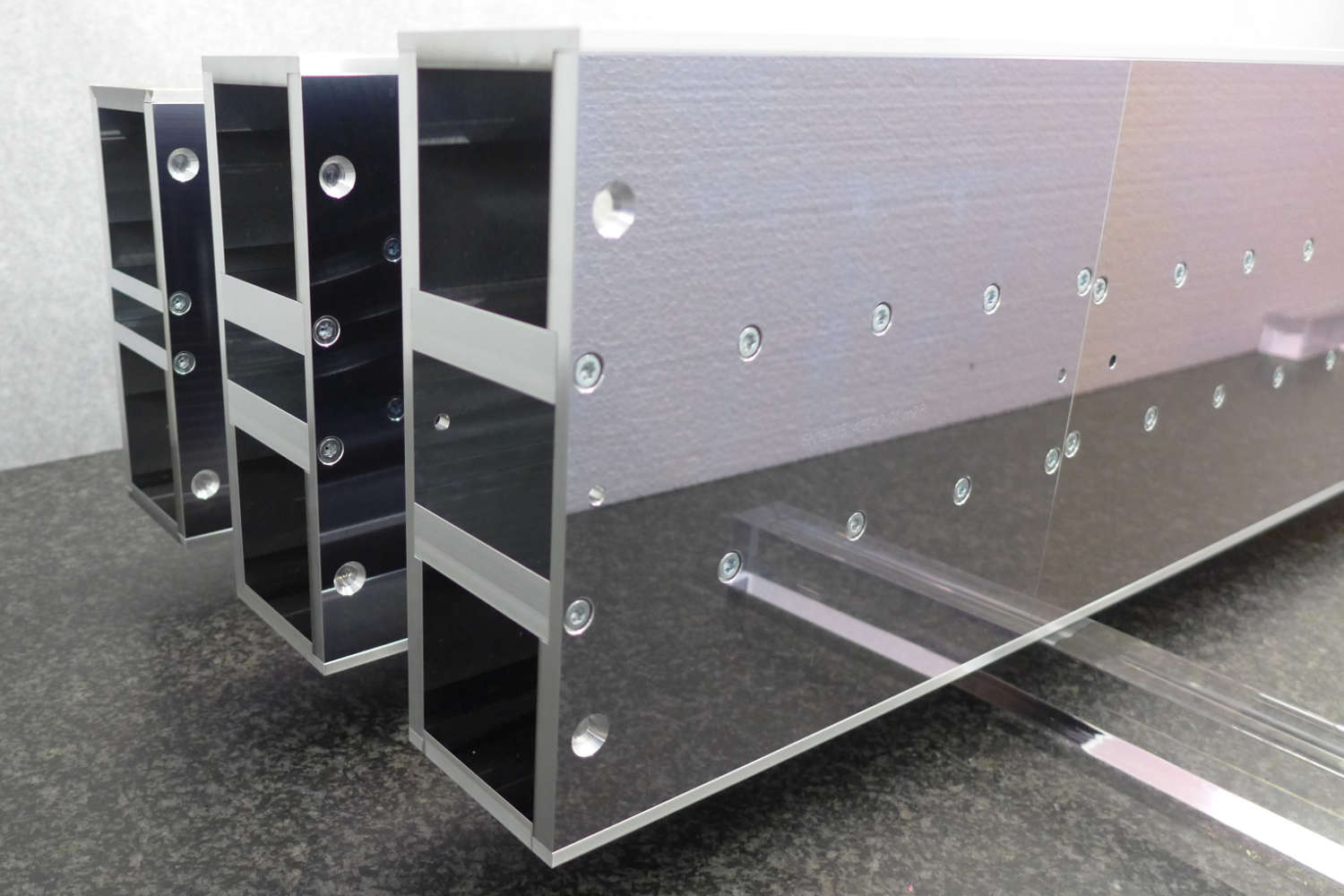
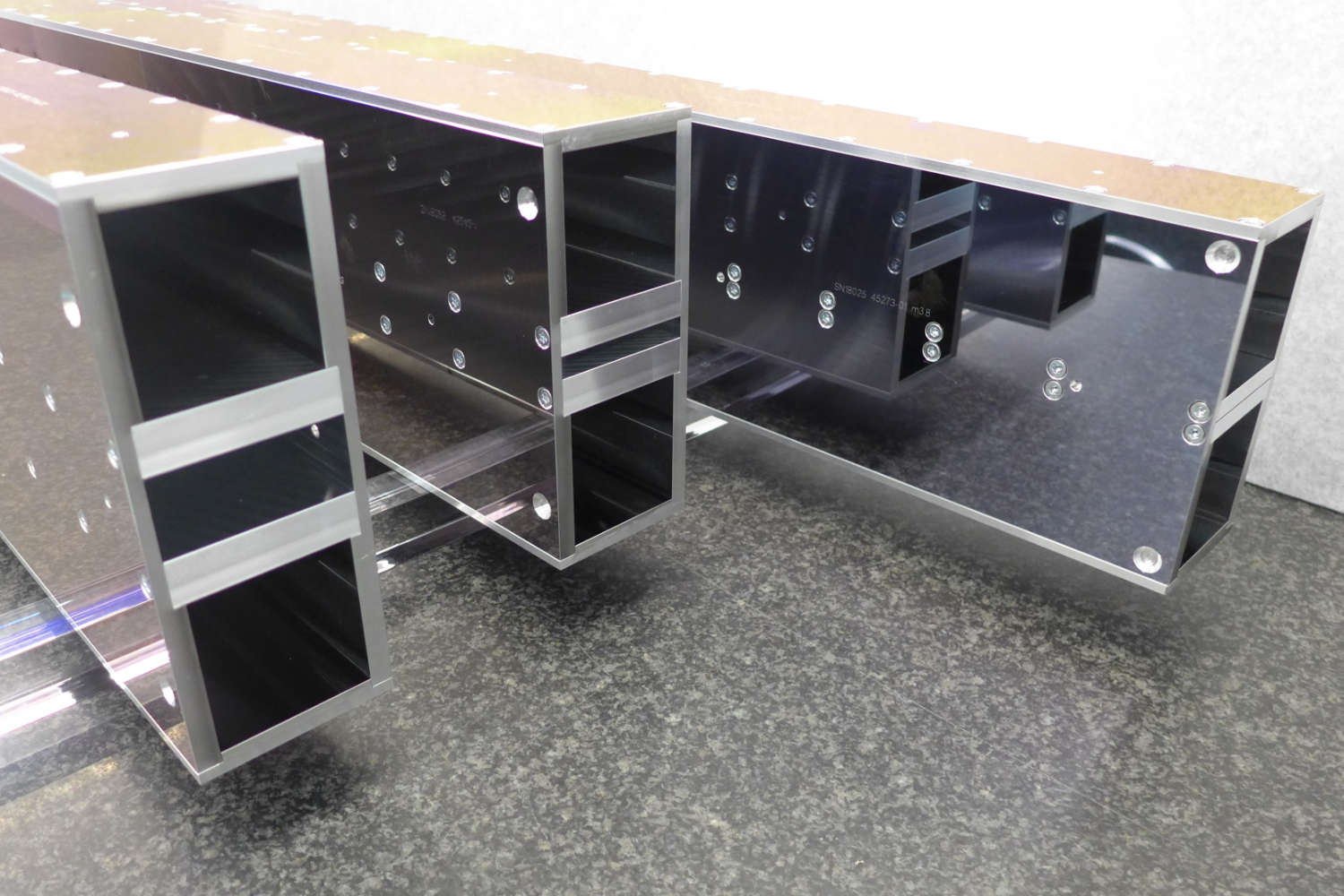
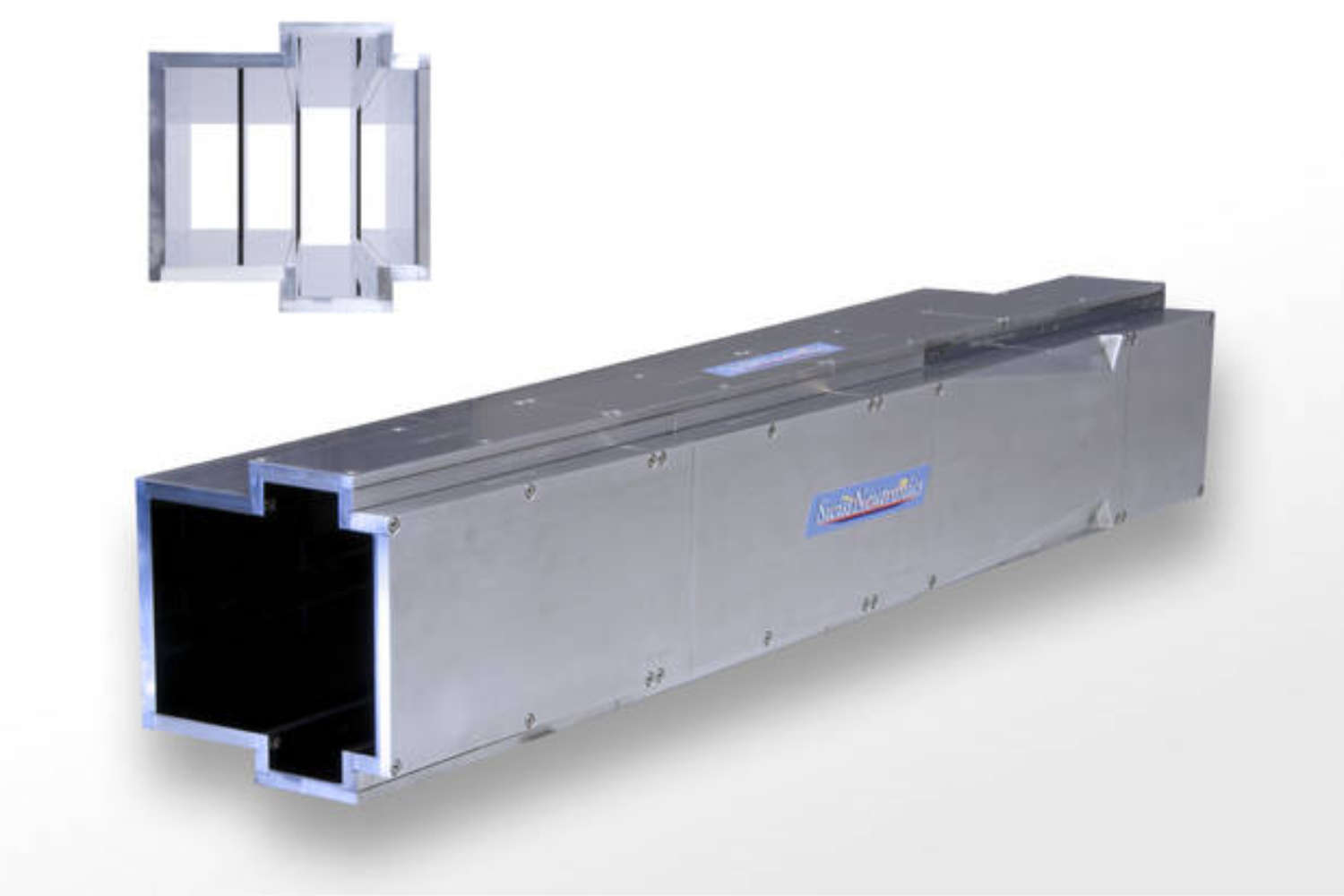
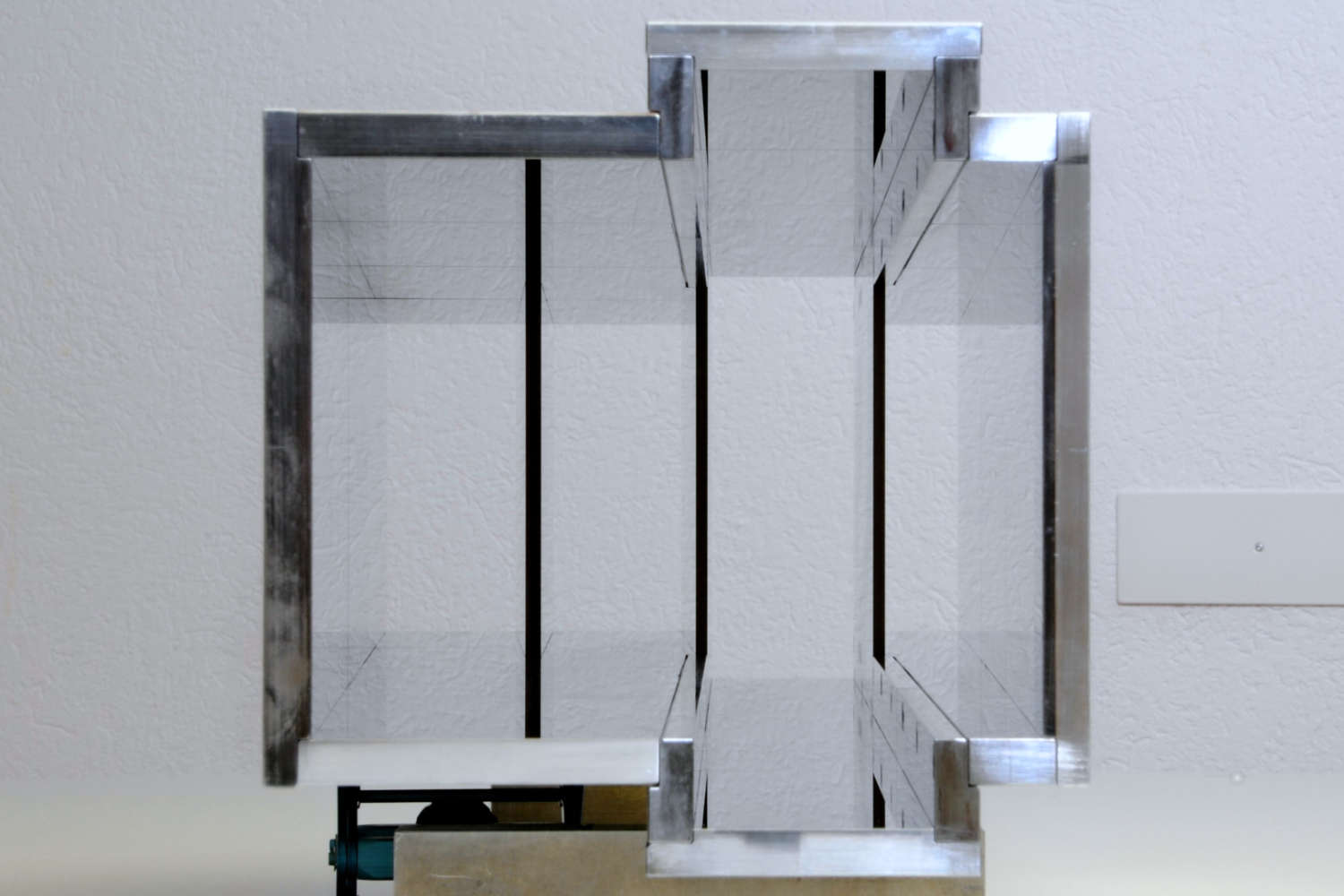
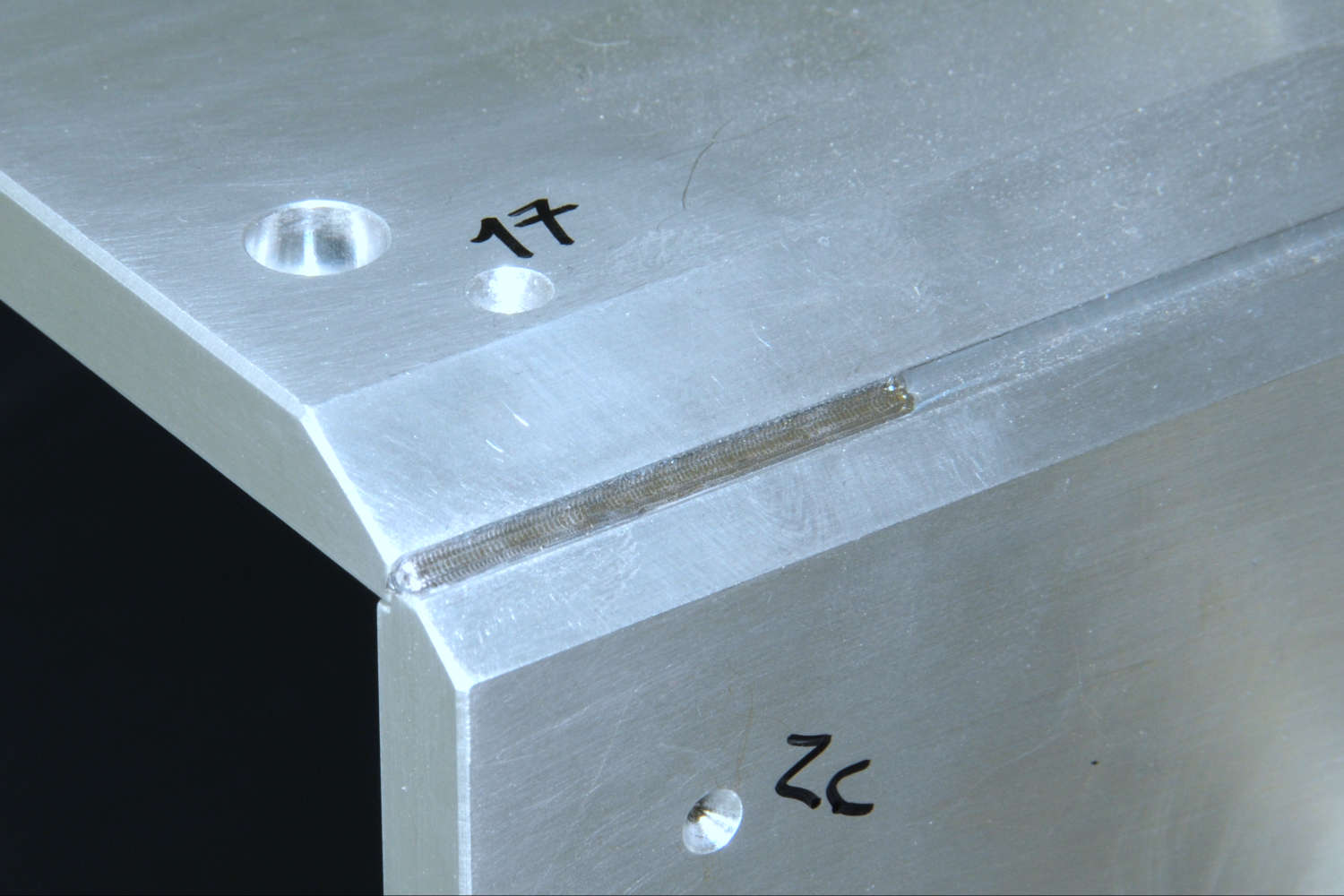
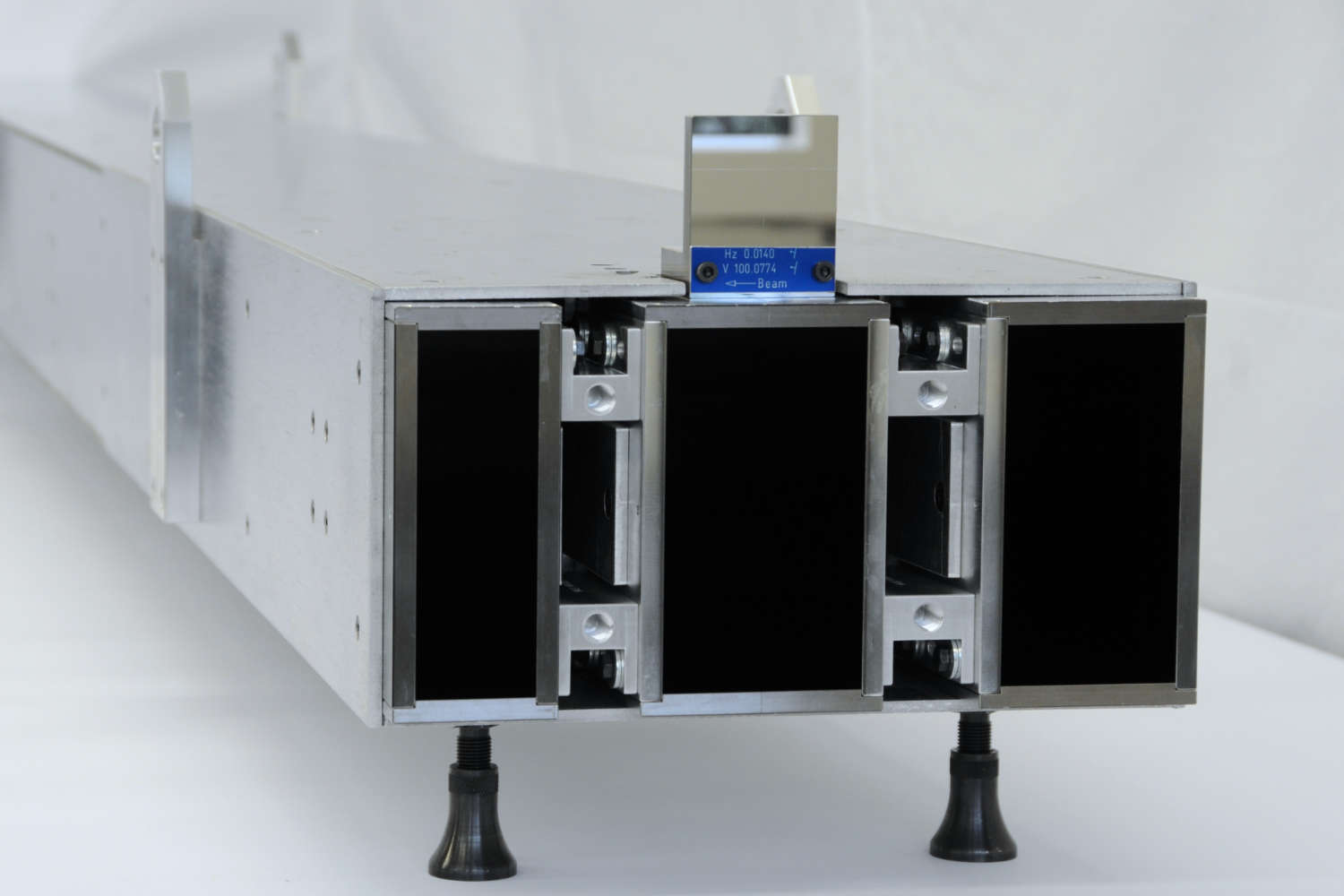
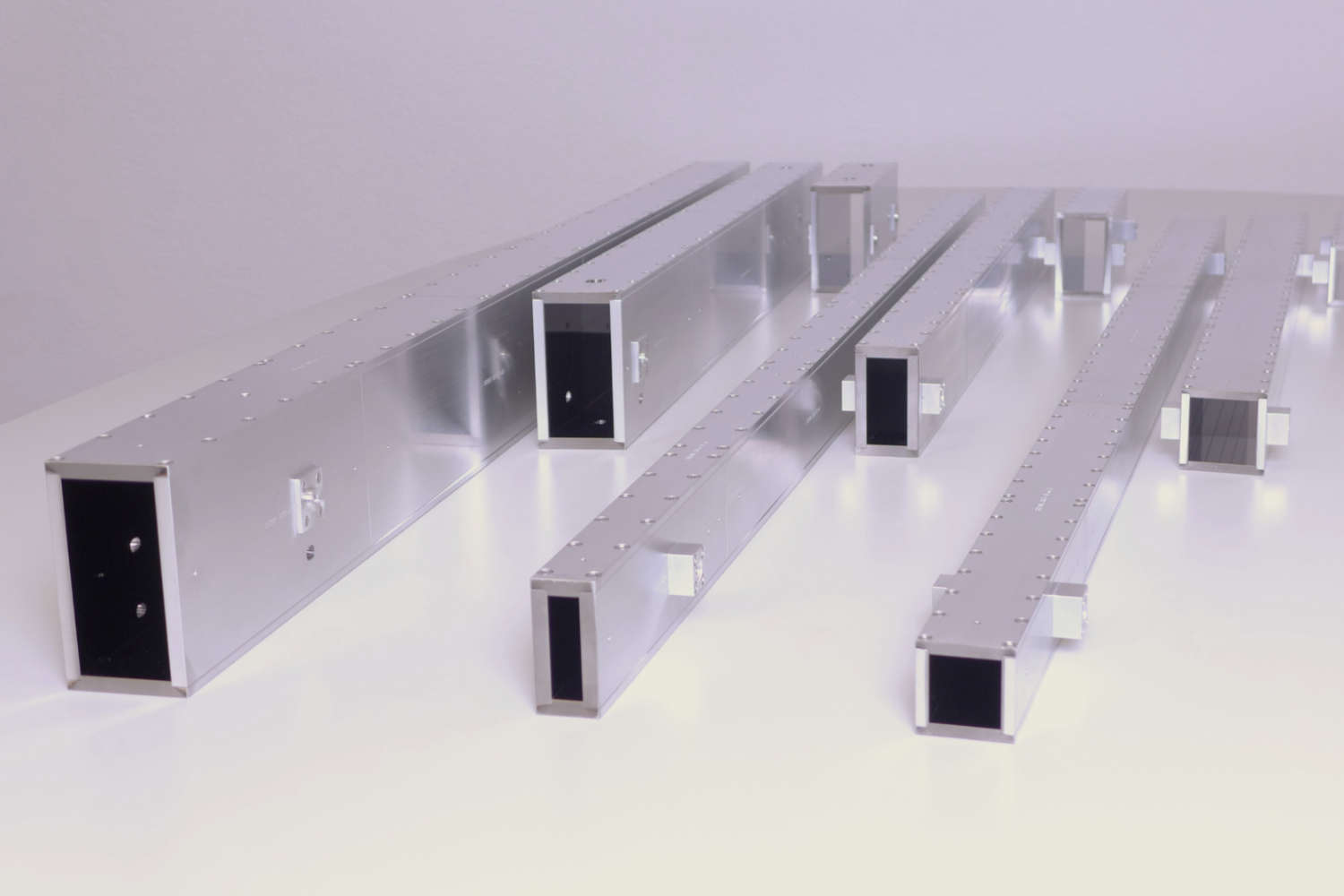
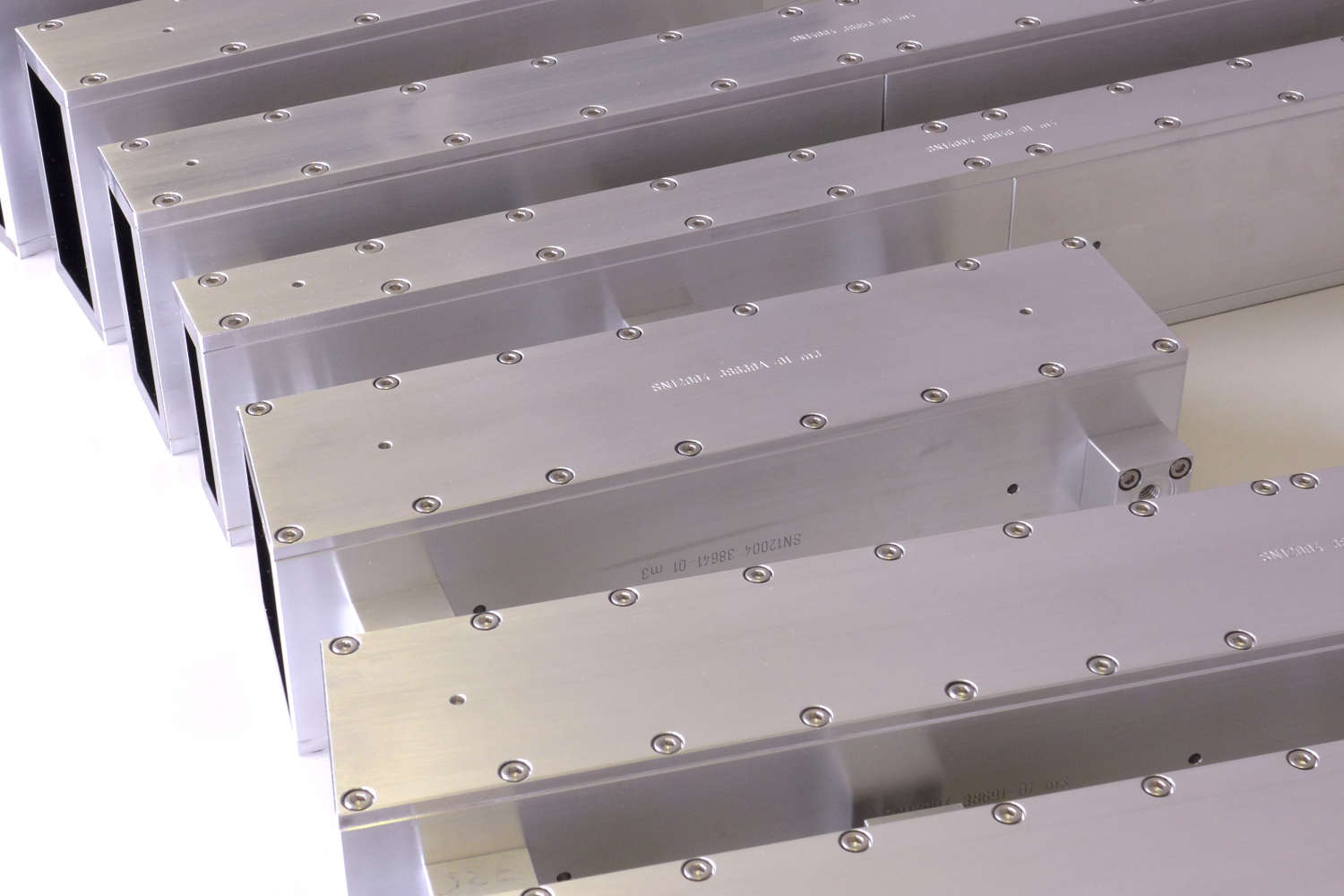
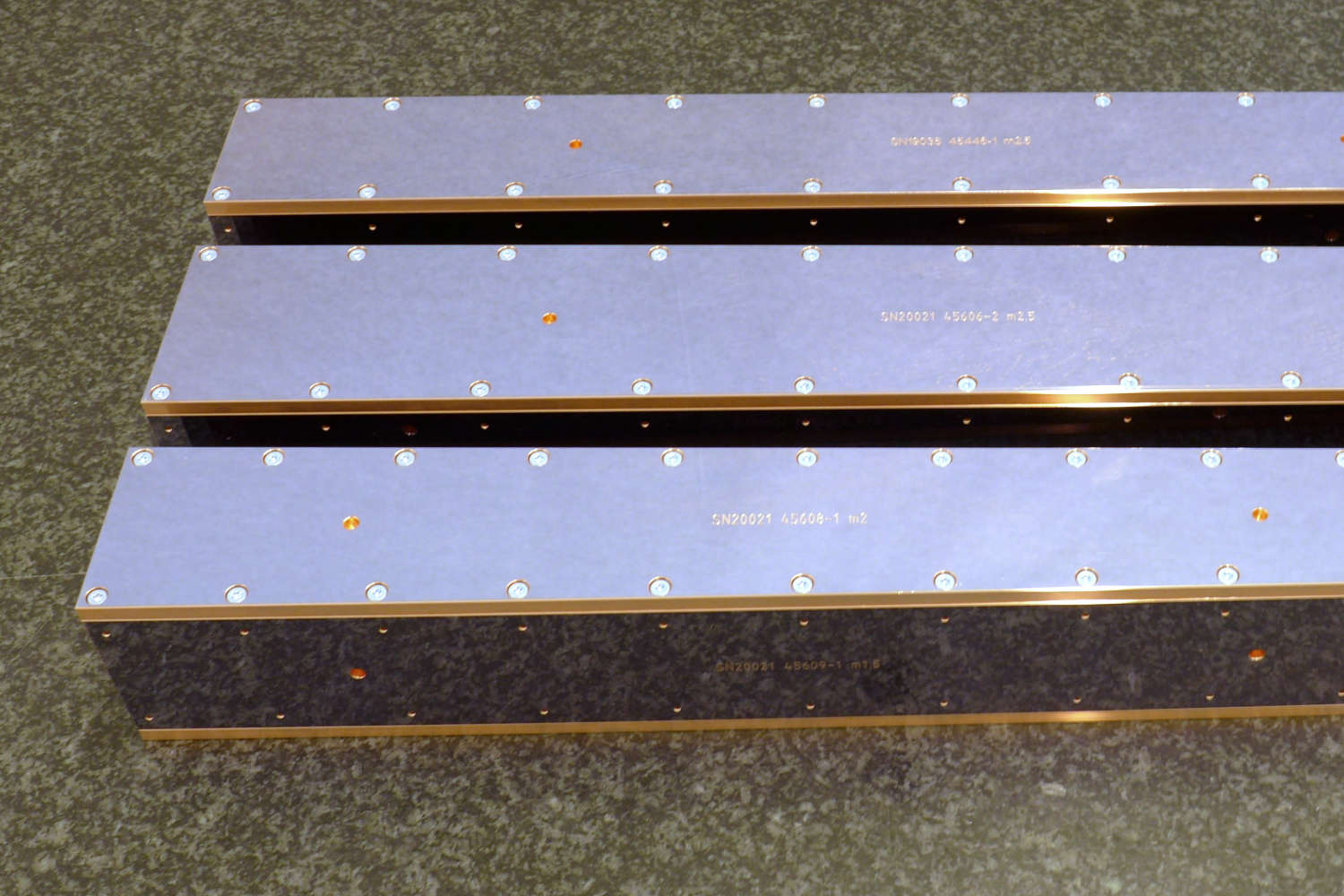
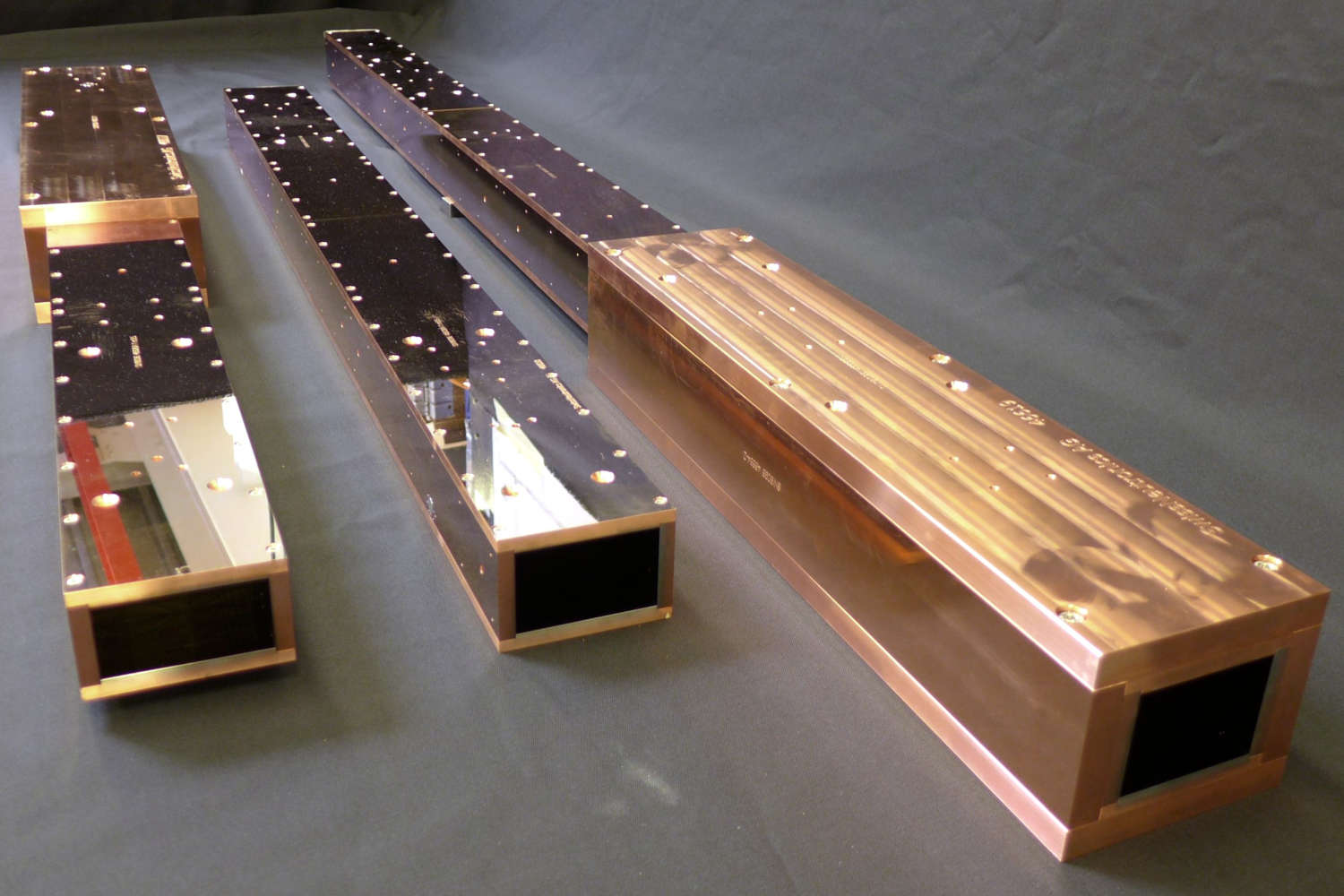
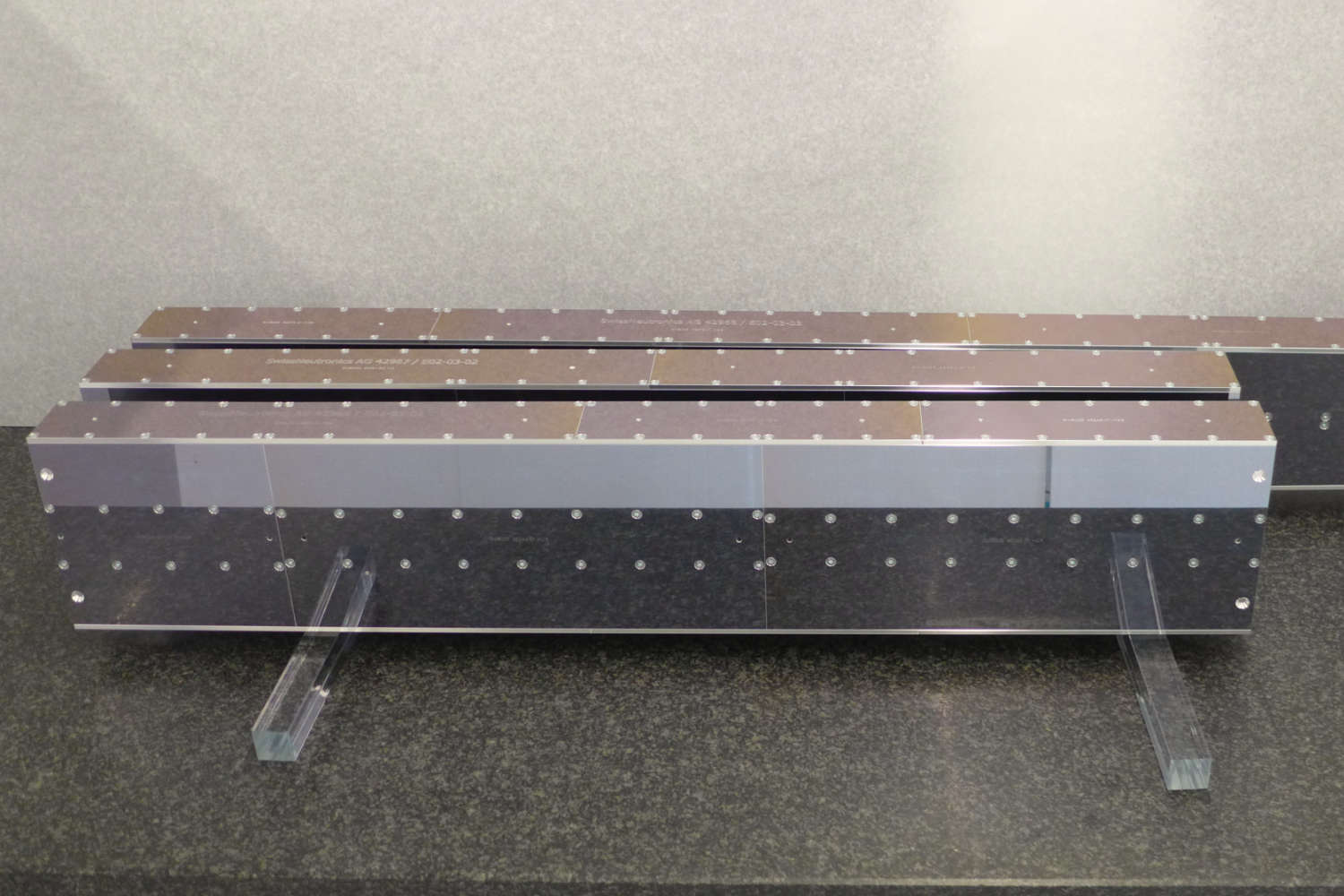
Substrates for demanding neutron guides – Metallic guides are essential components in advanced neutron guide systems. SwissNeutronics has developed a proprietary super-polishing process that significantly enhances the surface quality of metallic substrates. This refinement enables the application of high-performance neutron supermirror coatings with large m-values and excellent reflectivity. The result is a robust and efficient solution for demanding neutron optics applications.
Technical highlights
- Exceptional surface quality
Achieved roughness of approximately 1 Å RMS, comparable to super-polished glass, enables high reflectivity for neutron supermirror coatings - Scalable and reproducible fabrication
Suitable for large-scale production with consistent quality - Radiation stability
Proven resistance to degradation up to 9 × 10¹⁹ n/cm² - Mechanical robustness
Supports extended machining options, including welding - Functional versatility
Copper substrates offer highly efficient neutron shielding